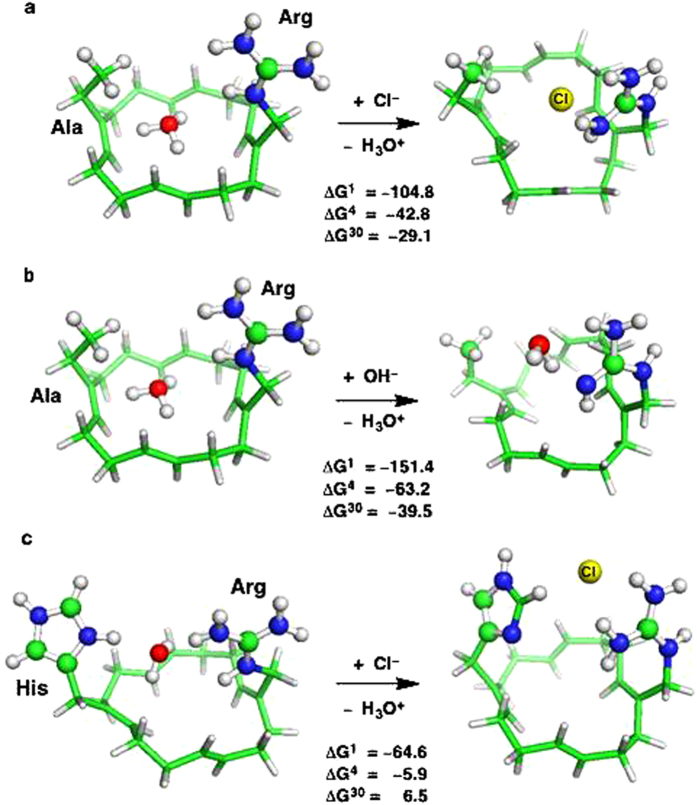
Figure 6. Binding of Cl– and/or OH– to H3O+-bound mutant SFs.
B3LYP/6-31+G(3d,p) fully optimized structures of H3O+–SF, Cl––SF and OH––SF complexes, and free energies (in kcal/mol) for (a) [SF(Ala-Arg+)-H3O+] + Cl– → [SF(Ala-Arg+)-Cl–] + H3O+, (b) [SF(Ala-Arg+)-H3O+] + OH– → [SF(Ala-Arg+)-OH–] + H3O+, and (c) [SF(His-Arg+)-H3O+] + Cl– → [SF(His-Arg+)-Cl–] + H3O+. ΔG1 is the ion exchange free energy in the gas phase, whereas ΔG4 and ΔG30 are the corresponding free energies in the SF characterized by an effective dielectric constant of 4 and 30, respectively. If the resulting free energy is negative, the pore is Cl– or OH–-selective, but if it is positive, the pore is proton-selective.