FIGURE 2.
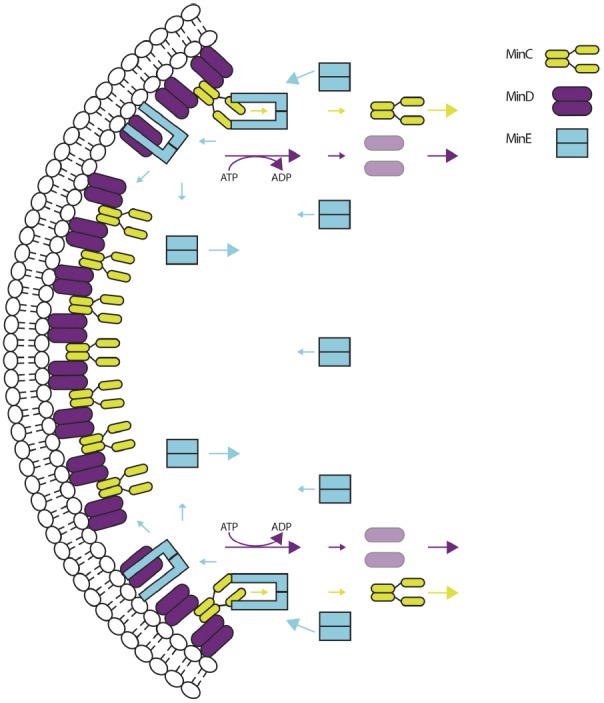
The molecular mechanism of Min oscillation. Membrane-bound complexes of MinC (chartreuse) and MinD (purple) are targeted by MinE (cyan). MinE dimers change conformation and bind MinD and the membrane, displacing MinC and stimulating the ATPase activity of MinD and its removal from the membrane. MinC and MinD-ADP move toward the opposite pole and begin another cycle of oscillation. MinE can stay membrane bound to remove more MinCD complexes, or change conformation and follow MinD to the opposite pole. Adapted from Rowlett and Margolin (2013).
