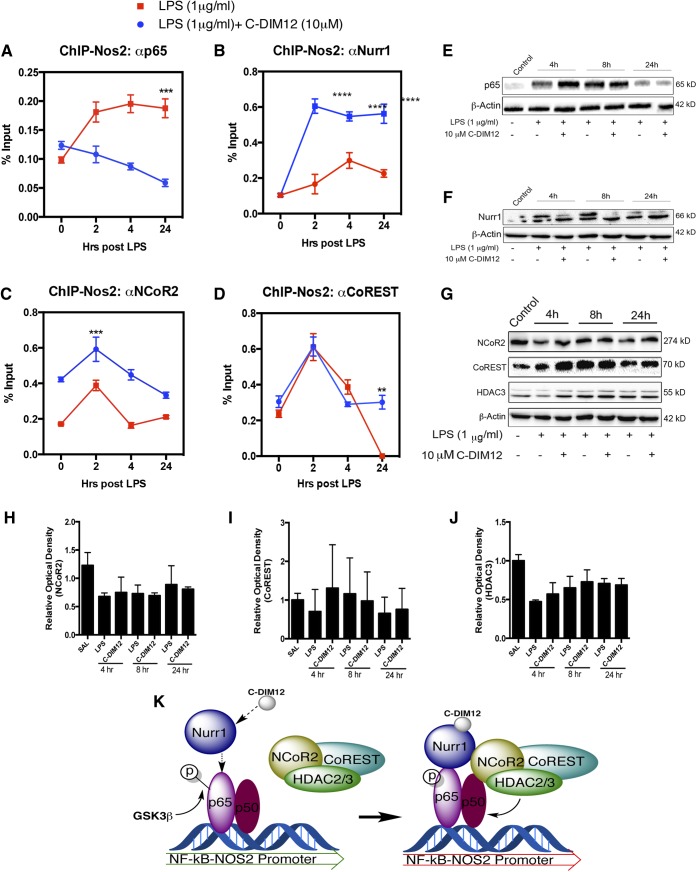
Fig. 6.
C-DIM12 enhances Nurr1 recruitment to NOS2 promoter, decreases p65 binding, and stabilizes binding of nuclear corepressors. BV-2 cells were treated with 10 μM C-DIM12 for 1 hour followed by 1 μg/ml LPS over a 24-hour time point and assessed at the NOS2 promoter using ChIP. (A) The amount of p65 bound to the NOS2 promoter was measured in LPS or LPS + C-DIM treatments. (B) The level of Nurr1 bound to the NOS2 promoter with or without C-DIM12 over a 24-hour time course with LPS. (C and D) ChIP assessment of nuclear corepressor NCOR2 and corepressor complex CoREST bound to the NOS2 promoter. (E and F) Representative protein quantitation of total Nurr1 and p65 after LPS and LPS + C-DIM12 treatment. (G) NCOR2, HDAC3, and CoREST protein from 24-hour time course treatment with saline or LPS + 10 μM C-DIM12. (H–J) Relative optical density of total cellular corepressor protein expression, mean of three replicate experiments. Protein levels were normalized to β-actin (±S.E.M.). (K) Hypothesized mechanism by which C-DIM12 promotes Nurr1-dependent transrepression of p65 at the NOS2 promoter in BV-2 microglia. ChIP data are expressed as the percentage of input ± S.E.M. over control IgG (n = 3). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. SAL, saline.