Abstract
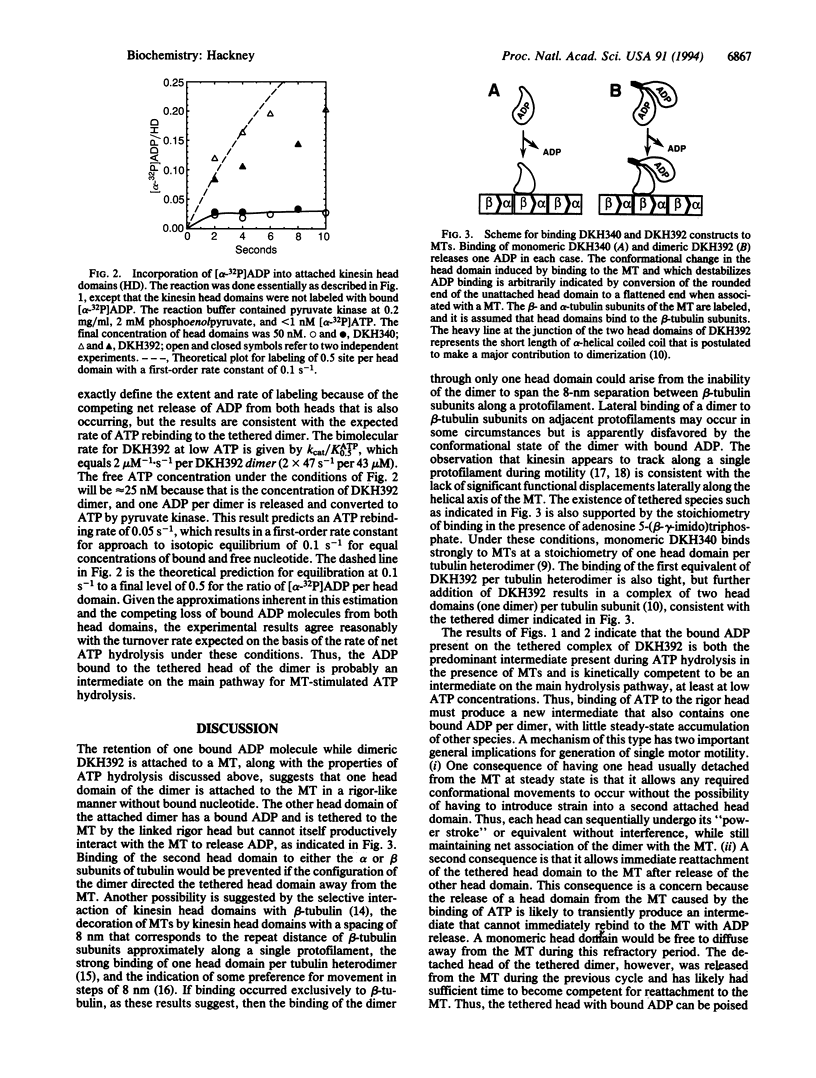
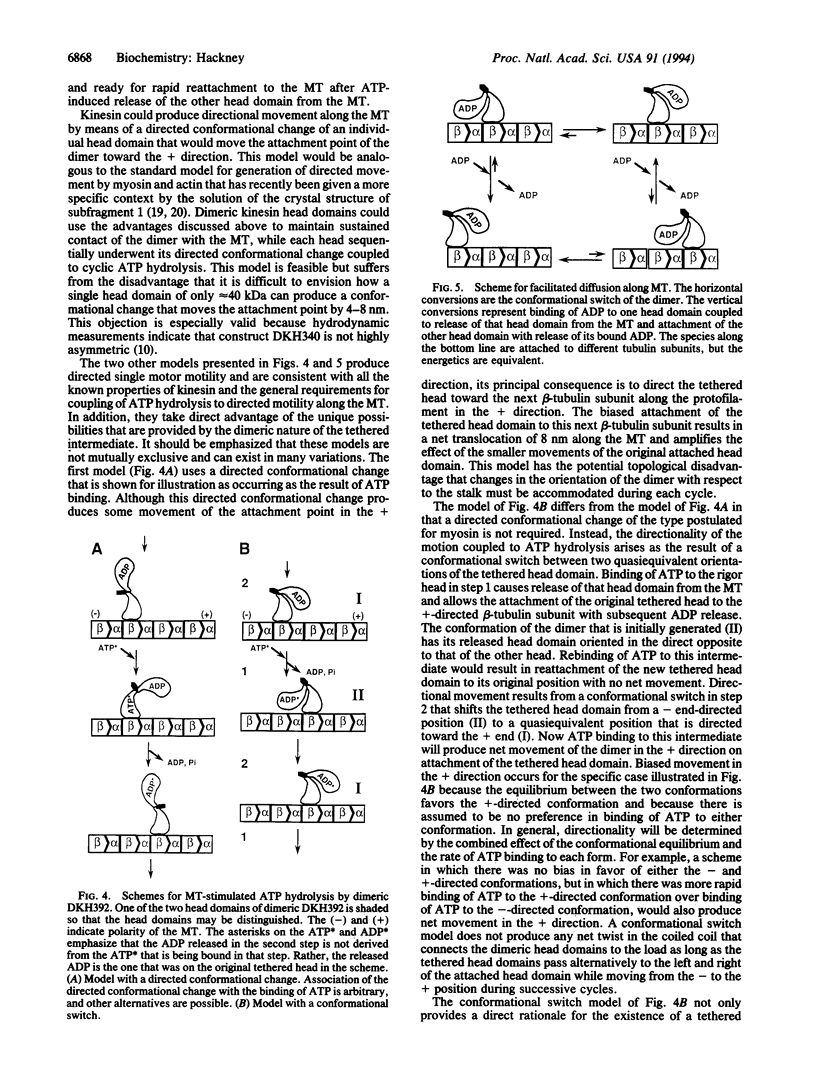
The N-terminal 392 amino acids of the Drosophila kinesin alpha subunit (designated DKH392) form a dimer in solution that releases only one of its two tightly bound ADP molecules on association with a microtubule, whereas a shorter monomeric construct (designated DKH340) releases > or = 95% of its one bound ADP on association with a microtubule. This half-site reactivity of dimeric DKH392 is observed over a wide range of ratios of DKH392 to microtubules and steady-state ATPase rates, indicating that it is characteristic of the mechanism of microtubule-stimulated ATP hydrolysis and not the result of a fortuitous balance of rate constants. When [alpha-32P]ATP is included in the medium, incorporation of 32P label into the pool of ADP that is bound to the complex of DKH392 and microtubules occurs rapidly enough for the bound ADP to be an intermediate on the main pathway of ATP hydrolysis. These and other results are consistent with the half-site reactivity being a consequence of the tethering of dimeric DKH392 to the microtubule through one head domain, which is attached in a rigor-like manner without bound nucleotide, whereas the other head is not attached to the microtubule and still contains a tightly bound ADP. An intermediate of this nature and the tight binding of DKH392 to microtubules in the presence of ATP suggest a mechanism for directed motility in which the head domains of dimeric DKH392 alternate in a sequential manner.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gelles J., Schnapp B. J., Sheetz M. P. Tracking kinesin-driven movements with nanometre-scale precision. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):450–453. doi: 10.1038/331450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. P., Johnson K. A. Expression, purification, and characterization of the Drosophila kinesin motor domain produced in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993 May 4;32(17):4677–4684. doi: 10.1021/bi00068a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D. Kinesin ATPase: rate-limiting ADP release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6314–6318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Levitt J. D., Wagner D. D. Characterization of alpha 2 beta 2 and alpha 2 forms of kinesin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):810–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Malik A. S., Wright K. W. Nucleotide-free kinesin hydrolyzes ATP with burst kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15943–15948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D. The rate-limiting step in microtubule-stimulated ATP hydrolysis by dimeric kinesin head domains occurs while bound to the microtubule. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16508–16511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison B. C., Marchese-Ragona S. P., Gilbert S. P., Cheng N., Steven A. C., Johnson K. A. Decoration of the microtubule surface by one kinesin head per tubulin heterodimer. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):73–75. doi: 10.1038/362073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J., Hudspeth A. J., Vale R. D. Movement of microtubules by single kinesin molecules. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):154–158. doi: 10.1038/342154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. G., Hackney D. D. Drosophila kinesin minimal motor domain expressed in Escherichia coli. Purification and kinetic characterization. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16493–16501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. G., Suhan J., Hackney D. D. Drosophila kinesin motor domain extending to amino acid position 392 is dimeric when expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16502–16507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hinkins S., Hartshorne D. J. Correlation of enzymatic properties and conformation of smooth muscle myosin. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4580–4587. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura S., Mandelkow E. Tubulin protofilaments and kinesin-dependent motility. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):865–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Vaisberg Y. A., Rothwell S. W., Murphy D. B., Gelfand V. I. Isolation of a 45-kDa fragment from the kinesin heavy chain with enhanced ATPase and microtubule-binding activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):589–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald H. B., Stewart R. J., Goldstein L. S. The kinesin-like ncd protein of Drosophila is a minus end-directed microtubule motor. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. M., Porter M. E., Cohn S. A., Scholey J. M., Raff E. C., McIntosh J. R. Drosophila kinesin: characterization of microtubule motility and ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1109–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y. H., Mandelkow E. Recombinant kinesin motor domain binds to beta-tubulin and decorates microtubules with a B surface lattice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1671–1675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Thaler J. P., Goldstein L. S. Direction of microtubule movement is an intrinsic property of the motor domains of kinesin heavy chain and Drosophila ncd protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5209–5213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Schmidt C. F., Schnapp B. J., Block S. M. Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):721–727. doi: 10.1038/365721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M., Huiatt T. W., Lowey S. A bent monomeric conformation of myosin from smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6151–6155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Shpetner H. S. Motor proteins of cytoplasmic microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:909–932. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]