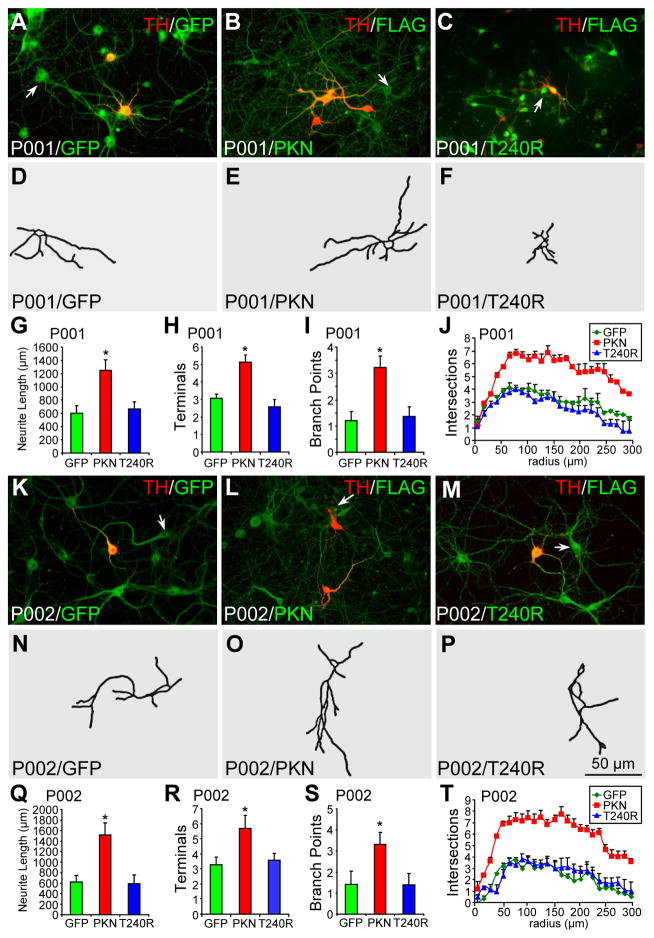
Figure 3.
Morphology of parkin-deficient TH− neurons infected with lentivirus expressing GFP, wild-type or mutant parkin. (A–J) P001 iPSC-derived neurons were infected with lentivirus expressing GFP (A), FLAG-parkin (B, PKN) or FLAG-T240R mutant parkin (C, T240R) and co-stained for TH and GFP (A) or TH and FLAG (B, C). Contour of TH− neurons identified by the arrow was traced in (D–F). Total neurite length per neuron (G), number of terminals per neuron (H), number of branch points per neuron (I) and Sholl analysis (J) were quantified. (K–T) P002 iPSC-derived neurons were infected with lentivirus expressing GFP (K), FLAG-parkin (L, PKN) or FLAG-T240R mutant parkin (M, T240R) and co-stained for TH and GFP (K) or TH and FLAG (L, M). Contour of TH− neurons identified by the arrow was traced in (N–P). Total neurite length per neuron (Q), number of terminals per neuron (R), number of branch points per neuron (S) and Sholl analysis (T) were quantified. Arrows, TH− neurons that were traced. Bar, 50 μm. *, p < 0.001, vs. GFP, n = 46 TH− neurons for each derivative line of P001 neurons in G–J and n = 47 TH− neurons for each derivative line of P002 neurons in Q–T, all from three independent experiments.