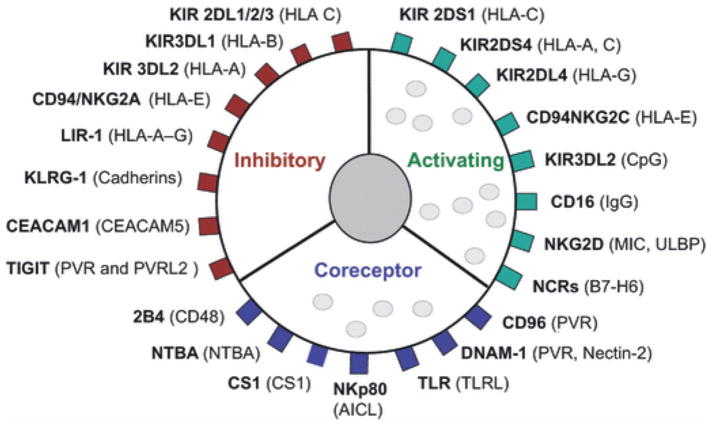
Figure 2.
NK cell surface receptors and their ligands. Receptors are broadly classified based on their primary function (inhibitory receptors, activating receptors, and activating co-receptors). Known ligands are denoted in parentheses. Despite the multitude of receptors shown, other families of receptors are not illustrated, including cytokine receptors (e.g., IL-1, IL-2, IL-12, IL-15, IL-18, IL-21, IFNα), chemotactic receptors (CCR2, CCR5, CXCR1, CXCR3, CXCR4, CXCR6, CX3CR1 and Chem23R), adhesion receptors (CD2 and β1 and β2 integrins), and inhibitory co-receptors (CD300A, LAIR-1 and Siglec7). Adapted with permission from: Wing Leung, Use of NK cell activity in cure by transplant, British Journal of Haematology 155, 14–29, 2011, Blackwell Publishing Ltd.