Figure 6. Sox2 negatively regulates Nf2 by binding to its promoter region.
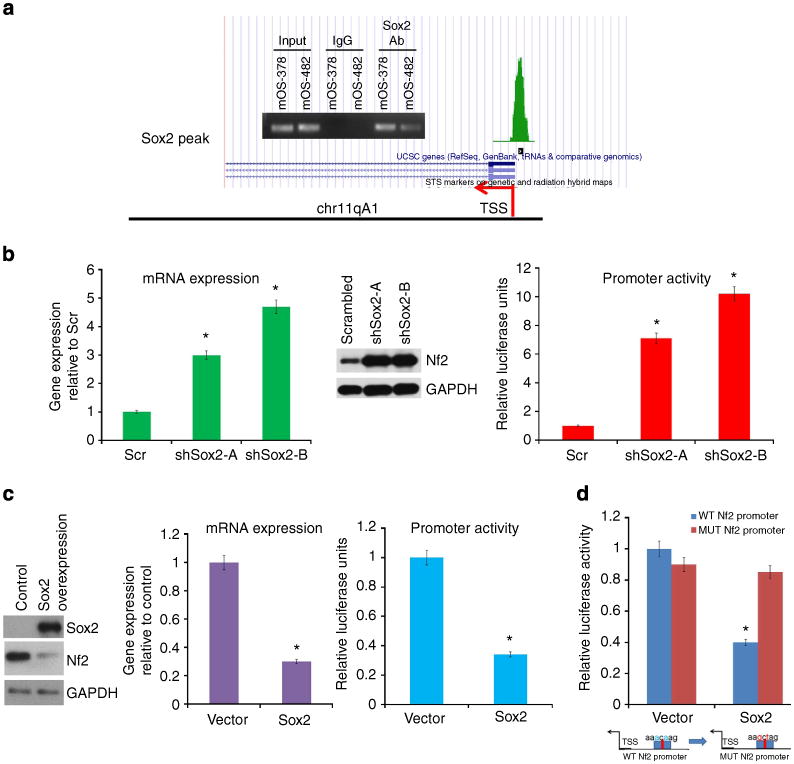
(a) Sox2 binds to the Nf2 5′ region. Sox2 ChIP-Seq shows one peak (green) of Sox2-bound genomic sequence in the Nf2 5′ region in Sox2-overexpressing osteoprogenitors29. Inset shows validation of ChIP-Seq in osteosarcoma cells by PCR analysis using primers flanking the Sox2-binding site in the Nf2 5′ region. (b) Analysis of Nf2 expression in mOS-482 cells expressing scrambled or two independent Sox2 shRNAs-A and B. Left panel: Nf2 mRNA expression normalized to actin levels. Middle panel: western analysis of Nf2 expression. Right panel: luciferase assay. A 1.5-kb fragment of the Nf2 promoter containing the Sox2-binding site was cloned into a pGL3-Basic luciferase vector. Activity of the Nf2 5′UTR luciferase reporter construct was normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. *P<0.05 by t-test. Error bars represent mean ± s.d. (c) Analysis of Nf2 expression in primary osteoblasts cells expressing control or Sox2 lentivirus. Left panel—Western analysis of Nf2 expression. Middle panel—Nf2 mRNA expression normalized to actin levels. Right panel—Luciferase assay. Activity of the Nf2 5′UTR luciferase construct was normalized to Renila luciferase activity. *= P<0.05 by t-test. Error bars represent mean ± s.d. (d) Sox2 binding is required for suppression of Nf2 expression. The Nf2 5′ promoter region has one Sox2-binding site. This was mutated in the Nf2 luciferase construct (used in b) and luciferase activity was measured and normalized to Renilla activity. *P<0.05 by t-test. Error bars represent mean±s.d. WT=wild-type promoter, MUT=promoter with a mutant Sox2-binding site. The mutated sites are shown in red in the schematic.
