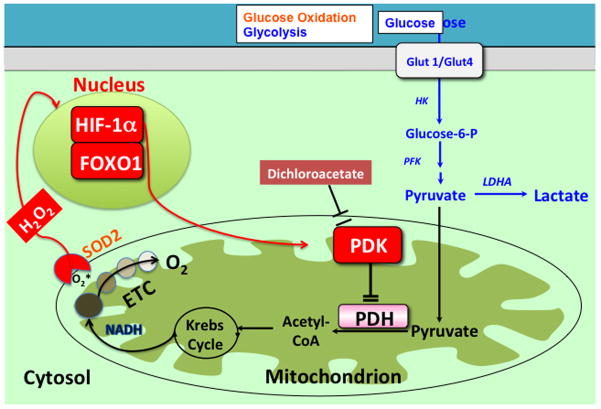
Figure 1.
Mechanism of impaired glucose oxidation and enhanced aerobic glycolysis in PAH. Changes in redox signaling, such as downregulation of SOD2 and the resultant decrease in H2O2 signaling, can activate transcription factors (i.e. HIF-1α) which in turn upregulate PDK. PDK inhibits PDH, which impairs oxidative glucose metabolism, causing the cell to rely on other forms of metabolism, such as aerobic glycolysis. The small molecular inhibitor of PDK, dichloroacetate, can reactivate PDH and restore oxidative glucose metabolism. Abbreviations: ETC = electron transport chain, FOXO1 = Forkhead box protein O1, HK = hexokinase, HIF-1α= Hypoxia inducible factor 1α, H2O2 = hydrogen peroxide, LDHA = lactate dehydrogenase A, PDH = Pyruvate dehydrogenase, PDK = Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, PFK = phosphofructokinase. Reprinted with permission from 2.