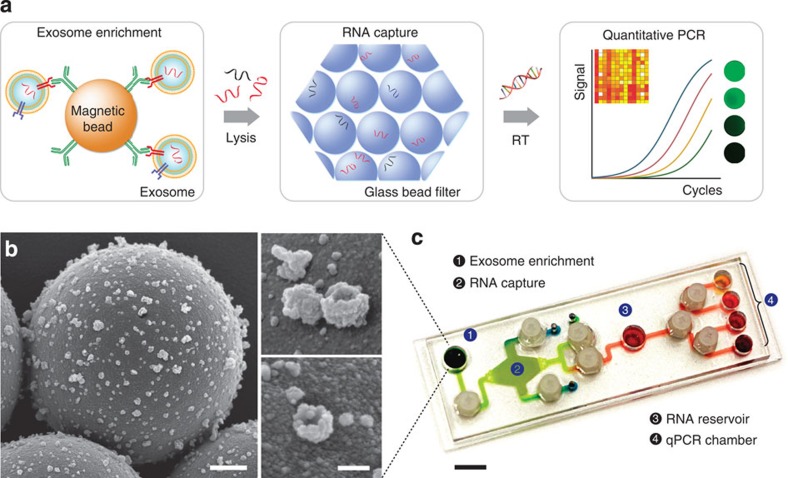
Figure 1. The immunomagnetic exosomal RNA (iMER) platform.
(a) The iMER platform is designed to enable exosome enrichment, RNA extraction, reverse transcription and real-time analyses of distinct RNA targets in one small device. Cancer exosomes in serum are first captured onto magnetic microbeads containing affinity ligands (for example, anti-CD63 and anti-EGFR). The immuno-enriched exosomal population is then lysed and the lysate flows through a glass bead filter, where RNA efficiently adsorbs onto packed glass beads. Finally, the collected RNA is eluted and reverse-transcribed for real-time amplification and quantitation. (b) Scanning electron micrographs of magnetic microbeads after immunoaffinity capture. Microbeads (left, 3 μm) functionalized with antibodies against EGFRvIII, a cancer-specific deletion mutant, captured innumerable tumour vesicles from GLI36vIII conditioned medium. High-magnification micrographs (right) show that many of the captured vesicles exhibit cup-shaped characteristic of exosomes. Scale bars, 500 nm, 100 nm (inset). (c) Photograph of the microfluidic iMER prototype. The cartridge was developed to house all components of the iMER procedure, including (1) an immunomagnetic capture site, (2) a filter composed of densely packed glass beads for RNA extraction, (3) a main reservoir for reverse transcription and (4) qPCR chambers for multiplexed detection. Scale bar, 1 cm.