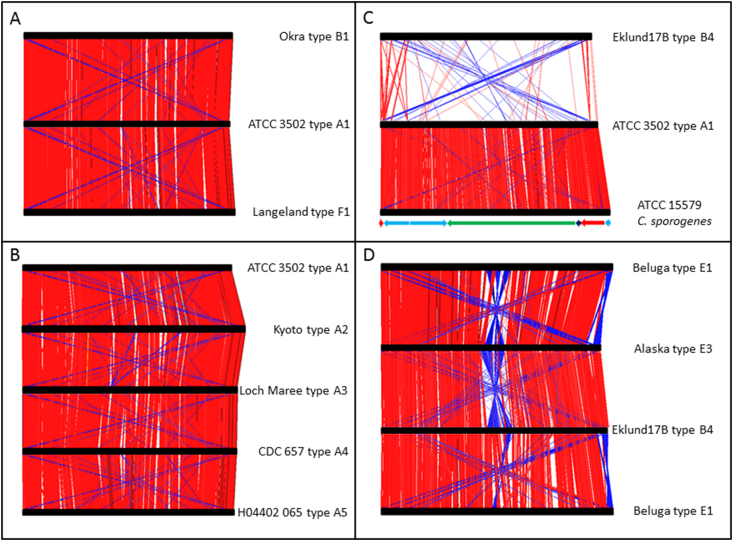
Fig. 2.
ACT comparisons of C. botulinum genomes. Red blocks indicate DNA homology (>90%) between paired genomes. Circular genomes are represented as linear horizontal black bars, with the gene annotated as coming first after each origin of replication positioned at the left hand end of each bar. A: C. botulinum Group I genomes of strains forming neurotoxins types A, B and F. B: C. botulinum Group I genomes of strains forming neurotoxin subtypes A1 – A5. C: Genomes of the C. botulinum Group I strain ATCC 3502, the C. botulinum Group II strain Eklund 17B, and the non-neurotoxigenic C. sporogenes ATCC 15579. Note that the contigs available in GenBank for the unfinished genome of C. sporogenes ATCC 15579 have been manually edited to generate a ‘best fit’ genome. The arrows below the black bar representing the genome of ATCC 15579 are coloured according to contig number: red, contig 488 (GenBank accession number ABKW02000002); light blue, contig 478 (ABKW02000003); green, contig 493 (ABKW02000004); dark blue, contig 486 (ABKW02000001). The arrows also indicate whether the contigs have been reverse/complemented in order to respect the genome of ATCC 3502, and that two contigs (478 and 488) have been broken apart, also in order to match this genome. D: Genomes of the C. botulinum Group II strains Beluga, Alaska and Eklund 17B. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)