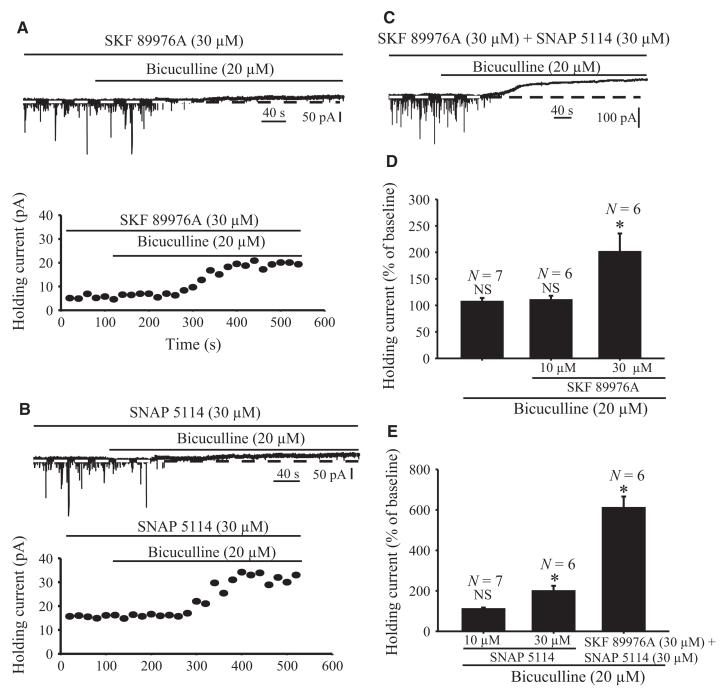
Fig. 9.
Application of GAT-1, GAT-3 or GAT-1 together with GAT-3 inhibitors induces GABAA receptor-mediated tonic currents in rat GP neurons. (A) Sample trace illustrates that application of bicuculline (20 μm) induces a tonic outward current in the presence of 30 μm SKF 89976A (top). Note that the sIPSCs are completely abolished by bicuculline in the presence of ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists, confirming that they are mediated by GABAA receptor activation. The bottom graph shows the time course of bicuculline-induced tonic currents in the presence of 30 μm SKF 89976A in the neuron displayed in the top trace. (B) Sample trace showing that application of bicuculline (20 μm) induces tonic outward current (top). The bottom panel displays the time course of this current in the presence of 30 μm SNAP 5114. (C) Sample trace showing that bicuculline induces tonic current in the presence of 30 μm SKF 89976A together with 30 μm SNAP 5114. (D–E) Summary bar graphs showing the effects of bicuculline alone, or together with SKF 89976A (10 and 30 μm) (top graph), SNAP 5114 (10 and 30 μm) or SKF 89976A plus SNAP 5114 (bottom), on holding current expressed as percentage of control. (*Significant difference from control, P = 0.001.) N, number of cells tested; NS, not significant.