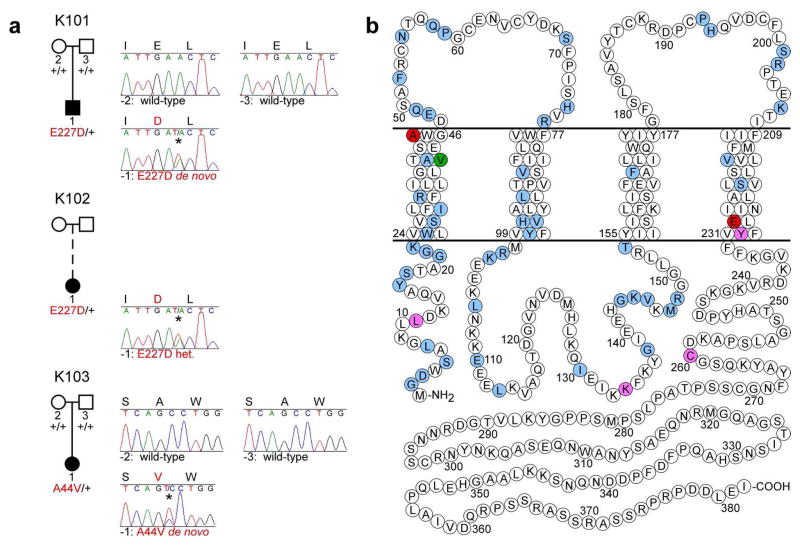
Figure 4. GJA1 mutations in EKVP kindreds.
(a) Affected and unaffected subjects are denoted with black and white symbols, respectively; adoption is shown with a dashed line. GJA1 alleles determined by sequencing of genomic DNA are denoted as ‘+’ (wild-type) or by the amino acid substitution in red (mutant). To the right of each pedigree, Sanger sequence traces at GJA1 mutation sites are shown for each subject and parents from whom DNA was available (mutant bases indicated with *). Amino acid sequences are shown at the top of each trace (mutant residues in red). Mutations are p.E227D, c.A681T (subjects 101-1 and 102-1) and p.A44V, c.C131T (subject 103-1) (NCBI RefSeq NM_000165). (b) Schematic model of Cx43 shows locations of mutations in EKVP patients reported here (red), and those reported in ODDD (blue), ODDD with palmoplantar hyperkeratosis (purple), and ODDD with Clouston syndrome (green).