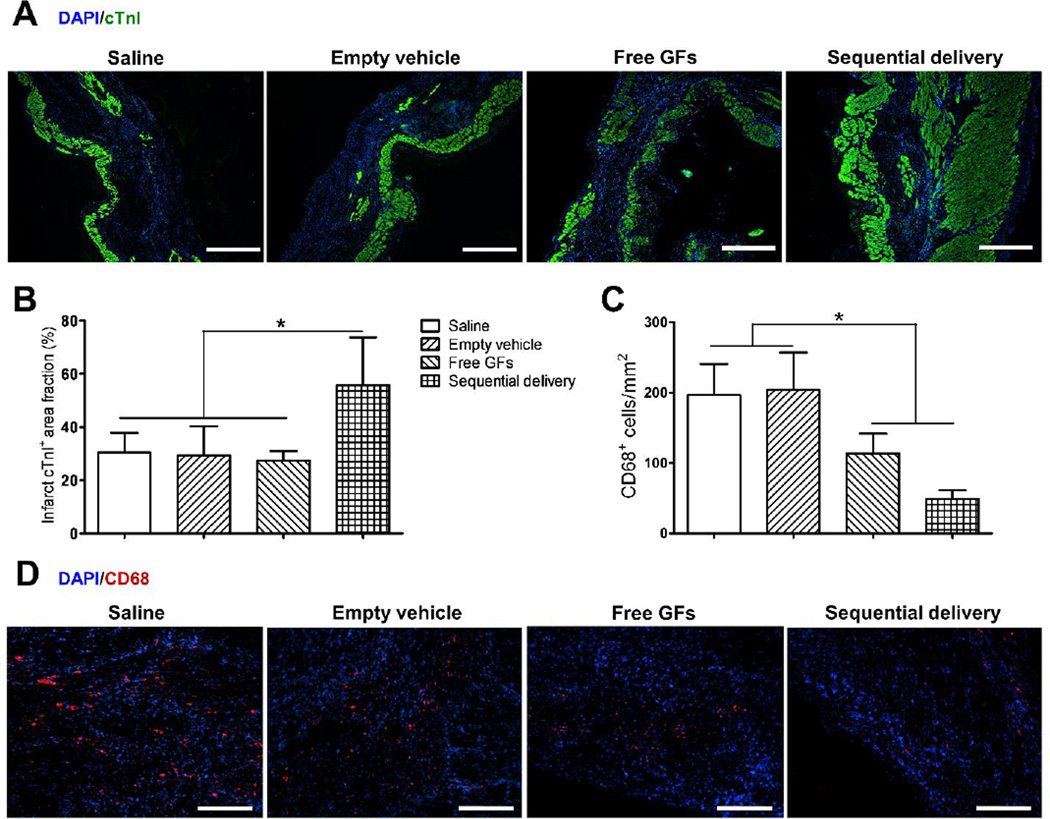
Fig. 7.
Sequential delivery of VEGF and PDGF improves cardiac muscle viability and reduces inflammation 4 wks after MI. (A) Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) staining (green) showed few viable cardiomyocytes in saline, empty vehicle, and free GFs groups, while sequential delivery group showed a larger area of viable cardiac muscle in the infarct zone. Scale bar=500 µm. (B) Quantitative analysis revealed that the sequential delivery group showed a significantly larger cTnI-positive area fraction in the infarct region compared to all groups. (C) Staining of inflammatory marker CD68 showed large numbers of CD68-positive cells in saline and empty vehicle groups, while significantly less cells were found in free GFs group and even less in sequential delivery group, with no significant difference between them. (D) Representative images of CD68 staining show less positive (red) cells in free GFs and sequential delivery groups. Scale bar=250 µm. Data are presented as means ± SD (n=4–5 per group). *P<0.05.