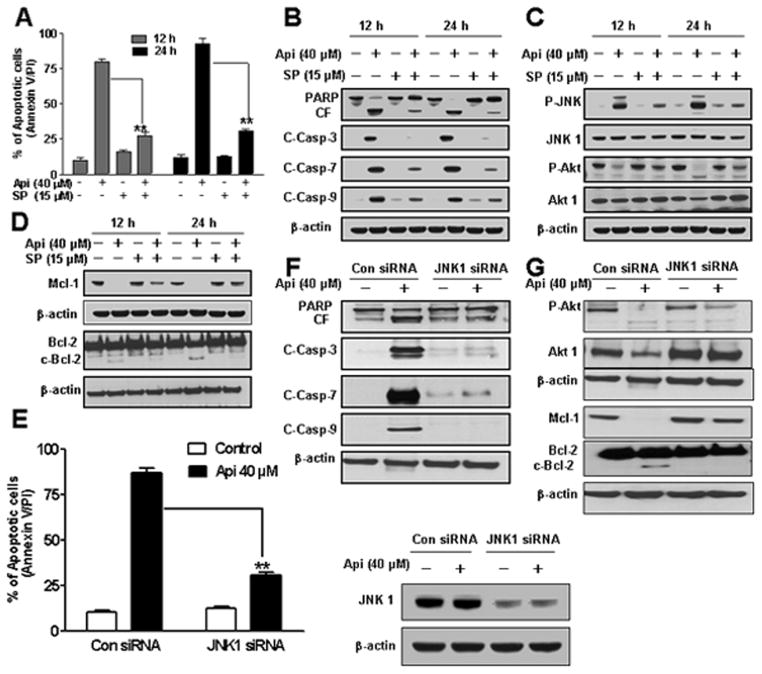
Fig. 5.
Effects of pharmacological and genetic inhibition of JNK on apigenin-induced apoptosis. U937 cells were pretreated with 15 μM SP600125 for 1 h followed by the addition of 40 μM of apigenin for 12 h and 24 h. (A) Cells were stained with Annexin V/PI and apoptosis was determined using flow cytometry. The values obtained from Annexin V assays represent the means ± SD for three separate experiments. **Values for cells treated with apigenin and SP600125 were significantly less than those obtained for cells treated with apigenin alone by Student’s t-test; p < 0.01. (B–D) Total cellular extracts were subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies. (E) U937 cells were transfected with JNK1 siRNA oligonucleotides or control siRNA and allowed to grow for 24 h, after which cells were treated with 40 μM of apigenin for another 24 h. Apoptosis was determined using the Annexin V/PI assay and JNK1 expression by western. **Values for cells treated with apigenin after transfection with JNK1 siRNA oligonucleotides were significantly decreased compared to those for control cells treated with apigenin alone by Student’s t-test; p < 0.01. (F–G) Total cellular extracts were subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies.