Figure 4.
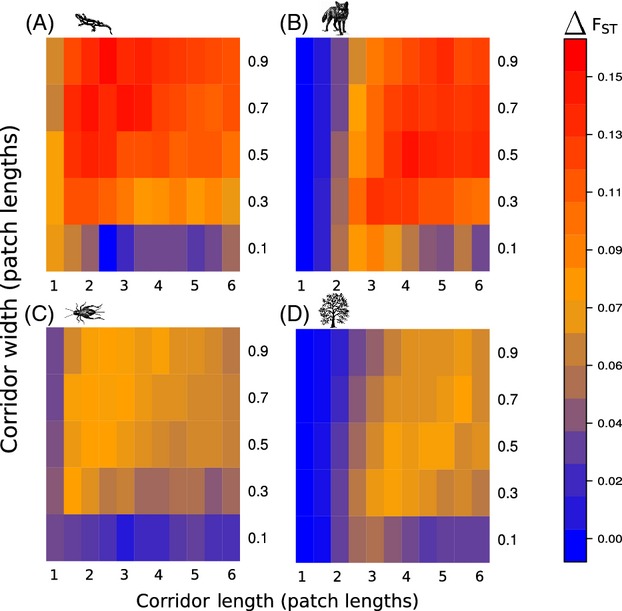
A heat map illustrating the differences in genetic differentiation (FST) between scenarios with high corridor mortality and those without increased corridor mortality (Panels A-D). Species with small population sizes experienced the largest increases in genetic differentiation (A and B) when exposed to high corridor mortality. Species with high dispersal distances were not substantially affected by corridor mortality at short corridor lengths (B and D). Notice that in most cases, corridor mortality resulted in an increase in genetic differentiation, which suggests that high-quality habitat corridors (those with low mortality) may be the most useful for mitigating the negative genetic effects of habitat fragmentation.
