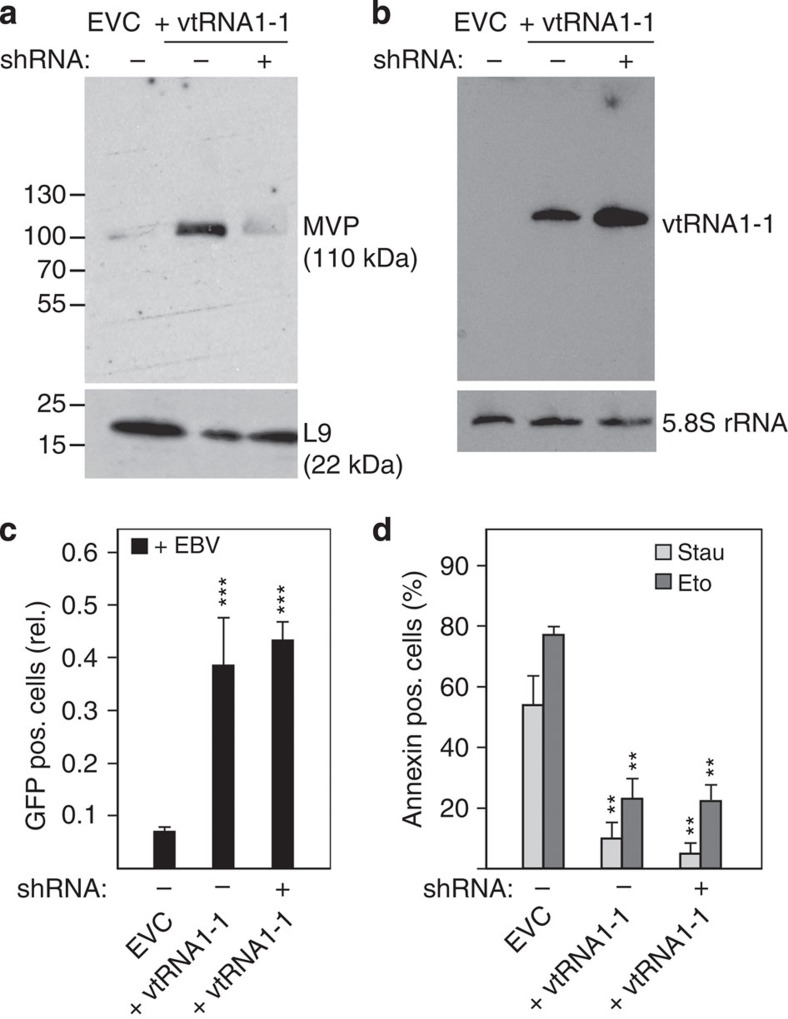
Figure 5. The vault complex does not contribute to the vtRNA1-1-mediated apoptosis resistance.
(a) MVP levels in BL41 cells treated with the empty vector control (EVC) or ectopically expressing vtRNA1-1 in the absence (+vtRNA1-1) or presence of shRNA directed against the MVP were probed by western blot analyses. Ribosomal protein L9 served as loading control. Locations of molecular weight markers (kDa) are shown on the left. See also Supplementary Fig. 9. (b) The expression levels of vtRNA1-1 in the cells shown in a were assessed by northern blotting. The 5.8S rRNA served as internal loading control. (c) The effects of MVP knockdown on infection with EBV strain 2089 were monitored by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. The data originates from four individual experiments. (d) Apoptotic cells after staurosporine (Stau) or etoposide (Eto) treatment in BL41 cells expressing vtRNA1-1 in addition to high or low levels of the MVP were assessed by annexin V staining and were recorded on FL2 on a FACS device. The data represent the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments. The amount of apoptotic cells in the untreated controls were <8% and were always subtracted from the staurosporine or etoposide treated cells. In c and d, significant differences relative (rel.) to the EVC were determined using the two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test (***P<0.001, **P<0.01). pos., positive.