Figure 7.
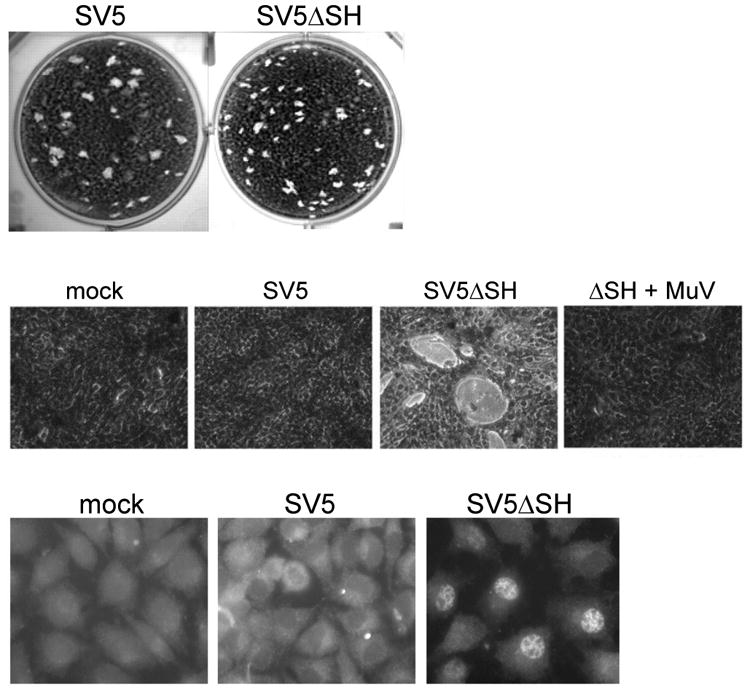
Effects on SH proteins on virus replication and apoptosis.(a) Permissive BSR-T7 cells were infected with wild-type recombinant simian virus 5 (SV5) or an SV5 mutant lacking the SH gene (SV5ΔSH), and plaque formation was assessed. (b) MBDK cells were mock infected, infected with wild-type SV5, infected with SV5ΔSH, or coinfected with SV5ΔSH and wild-type mumps virus (MuV), which express MuV SH protein (ΔSH + MuV). Photomicrographs were taken five days later. Note the marked cytopathic effect in cells infected with SV5ΔSH but not in the coinfected cells. (c) L929 cells were mock infected or infected with wild-type SV5 or SV5ΔSH. One day later, localization of NF-κB p65 was determined by immunofluorescence in permeabilized cells. Note nuclear translocation of NF-κB in cells infected with SV5ΔSH. Adapted from Reference 140 with permission from the American Society for Microbiology.
