Figure 2.
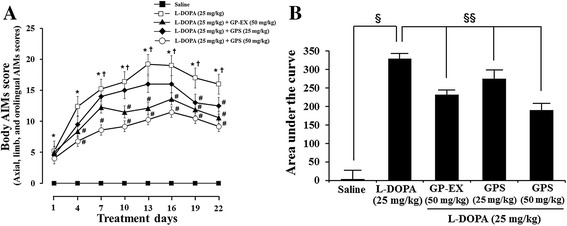
Effects of GPS and GP-EX on body AIMs score in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. L-DOPA (25 mg/kg, i.p.) and benserazide (15 mg/kg, i.p.) treatment was started 6 weeks after the 6-OHDA lesion once a day for 22 days. Either GPS (25 and 50 mg/kg, p.o.) or GP-EX (50 mg/kg, p.o.) was given 30 min prior to L-DOPA treatment once a day for 22 days. The axial, limb, and orolingual AIMs were calculated by adding each of the individual dyskinesia scores as body AIMs. A: body AIMs; B: area under the curve of body AIMs. The results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. for 8–10 animals/group. –■–, saline treatment; −□–, L-DOPA; −▲–, L-DOPA + GP-EX (50 mg/kg); −◆–, L-DOPA + GPS (25 mg/kg); −○–, L-DOPA + GPS (50 mg/kg). A: * P < 0.05 compared with saline-treated group at each treatment day; # P < 0.05 compared with L-DOPA alone-treated group at each treatment day (non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA test); † P < 0.05 compared with the score of day-1 (Friedman repeated measures ANOVA test), B: § P < 0.05 compared with saline-treated group; §§ P < 0.05 compared with L-DOPA alone-treated group (non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA test).
