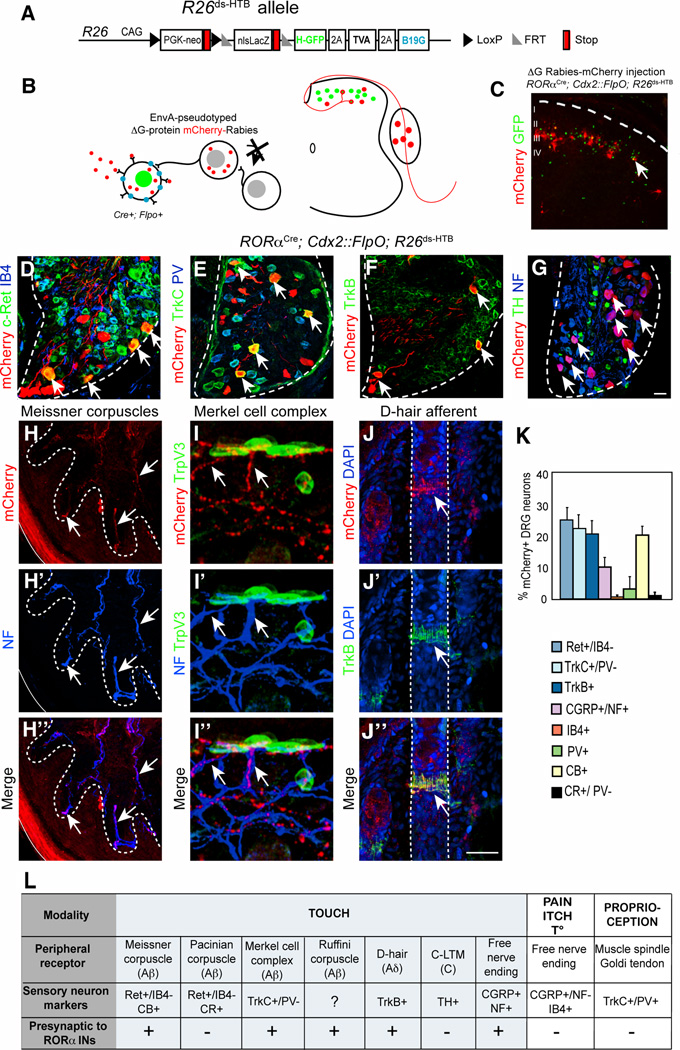
Figure 3. Transsynaptic rabies virus tracing of sensory inputs to RORα INs.
(A–B) Schematic showing the R26ds-HTB allele and strategy used for tracing monosynaptic inputs to the RORα INs using an EnvA-pseudotyped ΔG-mCherry-rabies virus. (C) Section through P10 RORαCre; Cdx2::FlpO; R26ds-HTB spinal cord showing mCherry-rabies virus labbled cells and RORα INs (green). mCherry+/GFP− cells represent transynaptically-labeled presynaptic neurons. (D–G) Sections from P10 RORαCre; Cdx2::FlpO; R26ds-HTB lumbar DRG showing presynaptically labeled sensory neurons and sensory neuron subtype markers as indicated (H) Section of hindlimb footpad stained with antibodies to mCherry (red) and NF (blue) showing Meissner corpuscles innervation. (I) Section of hindlimb hairy skin stained with antibodies to mCherry (red), NF (blue) and TrpV3 (green), which recognizes Merkel cells. (J) Section of hairy skin showing a D-hair afferent following staining with antibodies to mCherry (red), TrkB (green) and DAPI (blue) (K) Quantification of sensory neuronal markers in relation to total number of mCherry+ neurons, n = 3 mice. (L) Summary of sensory afferent types that are presynaptic to the RORα INs. Abbreviations: NF, neurofilament; CB, calbindin; CR, calretinin; TH, Tyrosine Hydroxylase. Dashed lines define the boundary of the DRG (D–G) and hair follicles (J). Arrows indicate double-labeled neurons or sensory afferents. Scale bar: 50 µm (D–G), 25 µm (H–J). See also Figure S3.