Figure 3.
Proteomics Identifies Neddylation-Dependent Ku Interactors
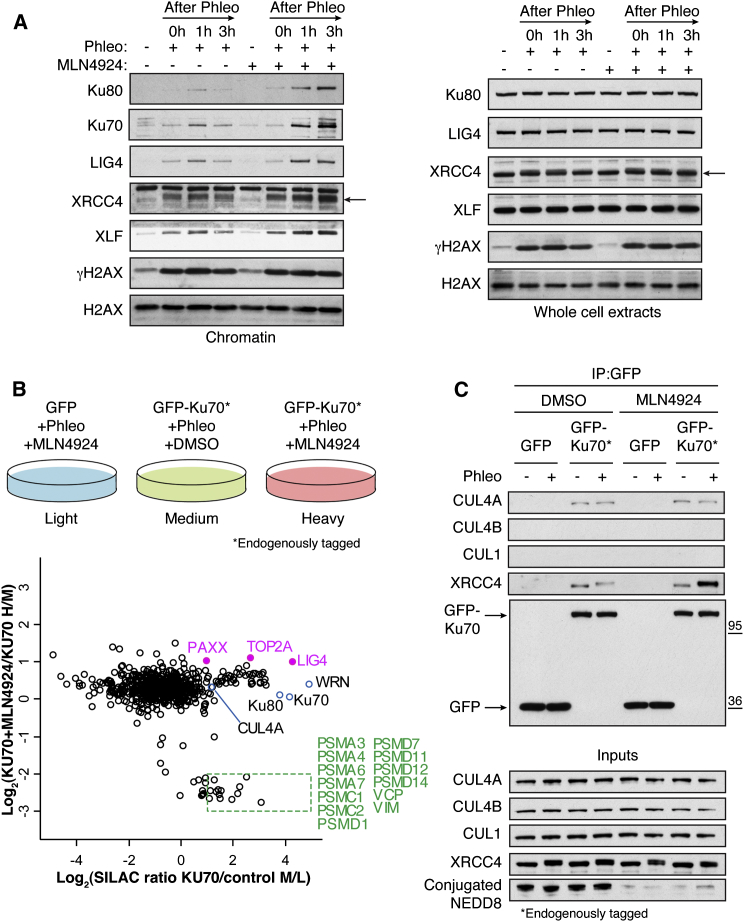
(A) MLN4924 causes retention of NHEJ factors on the chromatin. U2OS cells were pretreated with DMSO or 3 μM MLN4924 for 1 hr and then treated with 500 μM phleomycin (Phleo) for 1 hr. Cells were left to recover in the presence of MLN4924 or DMSO following phleomycin removal and then collected at the indicated times. Cells were pre-extracted with CSK buffer + RNase A prior to lysis (chromatin; left) or lysed as whole cell extracts (right) and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Black arrow indicates XRCC4.
(B) RPE-1 cells stably expressing GFP or Ku70 endogenously tagged with GFP were labeled with light, medium, or heavy isotopes and treated as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to GFP retrieval. Enriched proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and proteolysed in gel with trypsin, and peptides were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The scatterplot shows the logarithmized SILAC ratio of GFP-KU70/GFP control and GFP-KU70 + MLN4924/GFP-KU70. The known Ku interactors and CUL4A (ratio 2.23) are labeled in black font and open blue circles. In pink are interactions enhanced upon MLN4924. In green are interactions decreased upon MLN4924 (see also Table S1).
(C) Experiment repeated as in (B) without isotope labeling of cells. Following GFP IP, cell lysates were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Note that CUL1 (Postow and Funabiki, 2013) and CUL4B were not detected in Ku immunoprecipitates. See also Figure S3.