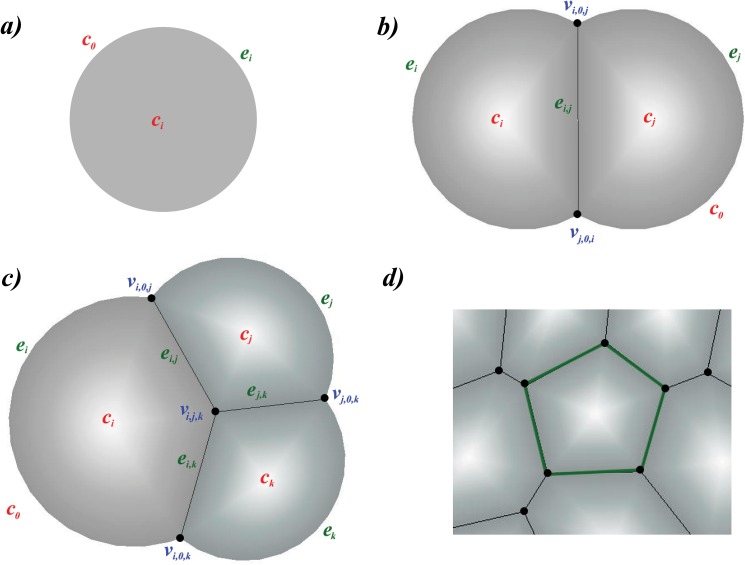
Fig 1. Two-dimensional cell model.
a) An isolated cell is modeled as a disk. b) A cell is modeled as a disk segment when contacting other cell(s). An outer edge e i is an arc or a circle, representing the boundary between cell c i and the outside medium (denoted as c 0). An inner edge e i,j occurs when a cell c i is in contact with another cell c j. Their shared boundary is modeled as a straight line segment. When two cells c i and c j make contact, their outer edges (arcs) e i and e j intersect at two vertices v i,0,j and v j,0,i, which are also the two end-points of the inner edge e i,j. c) When three cells c i,c j and c k intersect, they form a vertex v i,j,k. d) A cell completely surrounded by other cells is represented as a polygon.