Abstract
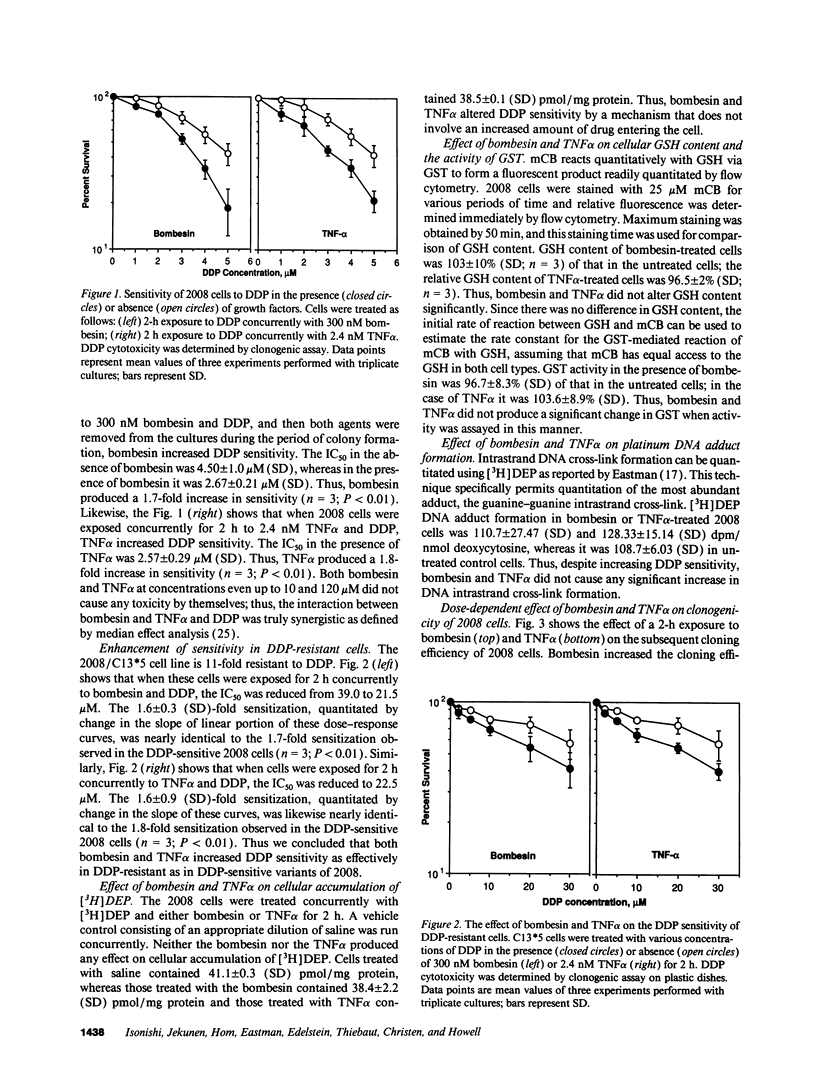
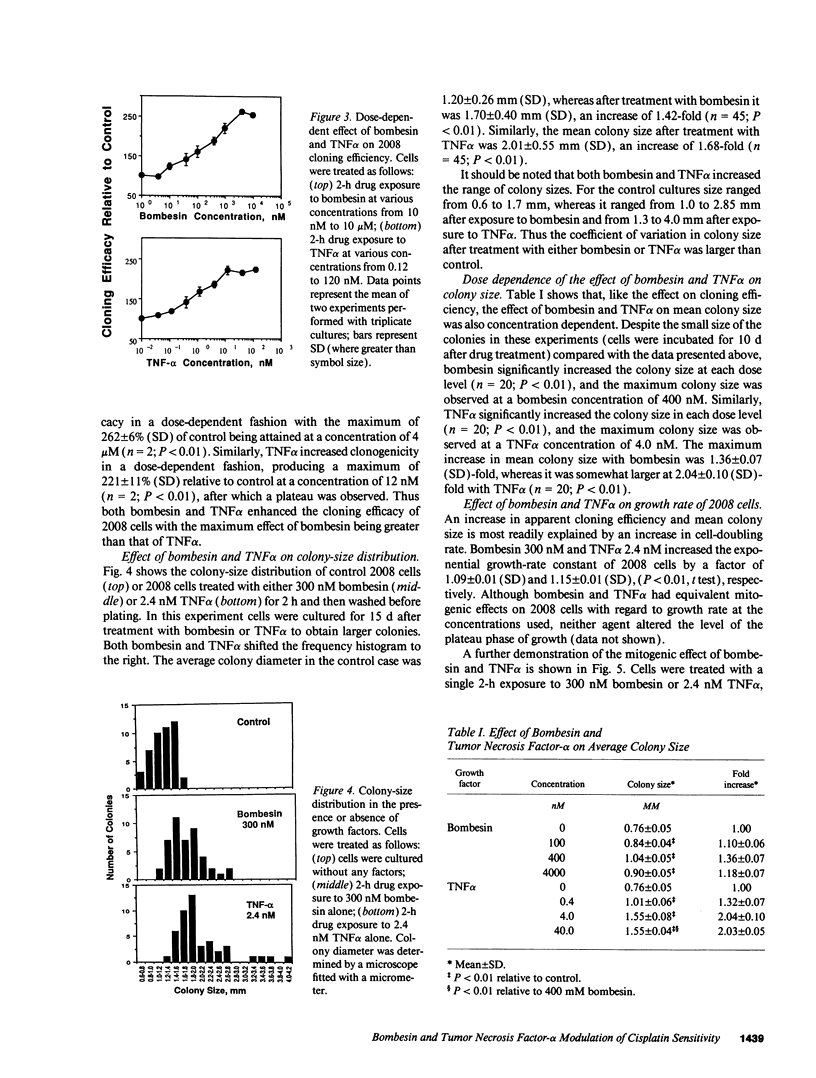
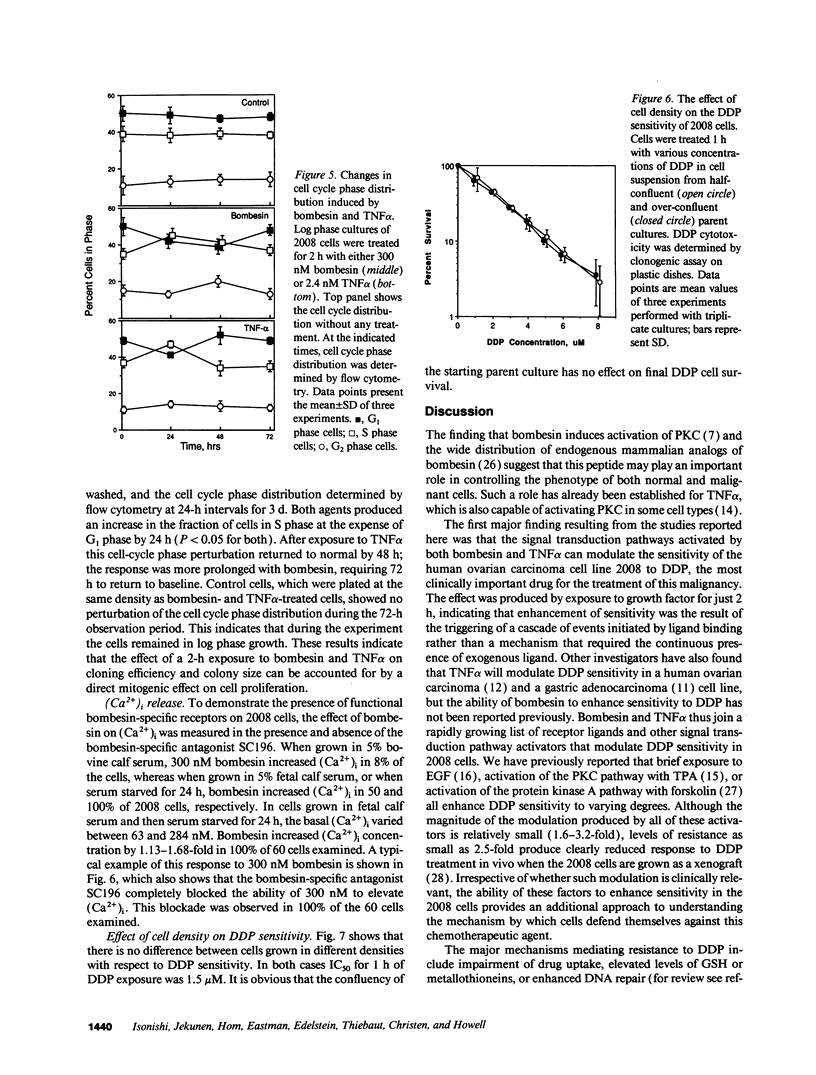
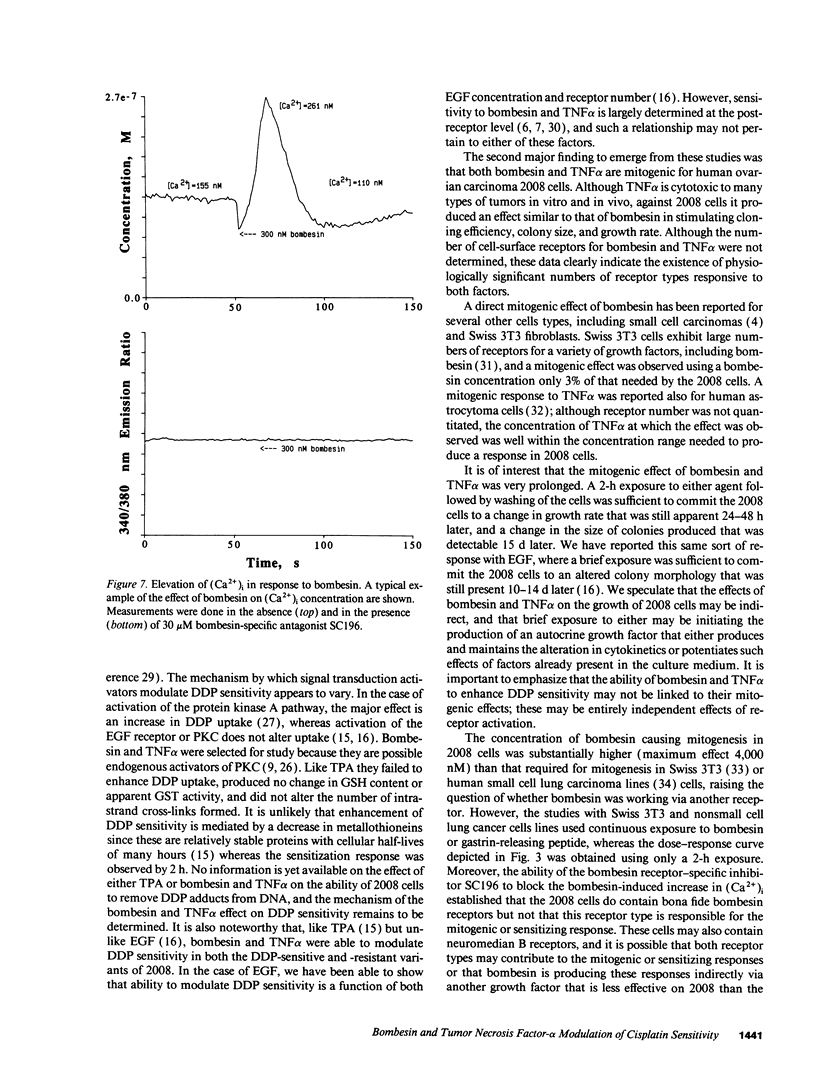
A twofold change in the cisplatin (DDP) sensitivity of 2008 human ovarian carcinoma cells is sufficient to reduce tumor response in vivo. The DDP sensitivity of these cells can be enhanced by activation of the epidermal growth factor and protein kinase C signal transduction pathways. We report here that two endogenous growth factors, bombesin and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha), enhanced DDP sensitivity by factors of 1.7 +/- 0.1 (SD)-fold and 1.8 +/- 0.1 (SD)-fold, respectively. Both agents also produced sensitization in an 11-fold DDP-resistant 2008 subline. Neither bombesin nor TNF alpha changed the accumulation of DDP, glutathione content, or glutathione-S-transferase activity in 2008 cells. However, a 2-h exposure to both bombesin and TNF alpha was sufficient to increase 2008 cloning efficiency by up to 2.6 +/- 0.1 (SD)-fold and 2.2 +/- 0.1 (SD)-fold, and it increased average colony size by 1.35 +/- 0.1 (SD)-fold and 1.55 +/- 0.1 (SD)-fold, respectively. Bombesin increased intracellular free calcium, and this was blocked by the bombesin receptor-specific antagonist SC196, demonstrating that 2008 cells have functional bombesin receptors. These results indicate that bombesin and TNF alpha can enhance sensitivity to DDP in both DDP sensitive and resistant variants of a human ovarian carcinoma and that both agents serve as growth factors for this tumor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasi A., Erspamer V., Bucci M. Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, 2 analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia. 1971 Feb 15;27(2):166–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02145873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. A., Jones J. A., Varki N. M., Howell S. B. Rapid emergence of acquired cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) resistance in an in vivo model of human ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 1990;2(2):93–100. doi: 10.3727/095535490820874641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. A., Murphy M. P., Howell S. B. Differential potentiation of alkylating and platinating agent cytotoxicity in human ovarian carcinoma cells by glutathione depletion. Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;45(12 Pt 1):6250–6253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. A., Schiefer M. A., Murphy M. P., Howell S. B. Enhanced potentiation of cisplatin cytotoxicity in human ovarian carcinoma cells by prolonged glutathione depletion. Chem Biol Interact. 1988;65(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(88)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., Cuttitta F., Moody T. W., Minna J. D. Selective stimulation of small cell lung cancer clonal growth by bombesin and gastrin-releasing peptide. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. C., Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:27–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen R. D., Hom D. K., Porter D. C., Andrews P. A., MacLeod C. L., Hafstrom L., Howell S. B. Epidermal growth factor regulates the in vitro sensitivity of human ovarian carcinoma cells to cisplatin. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1632–1640. doi: 10.1172/JCI114885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. K., Walther P. J., Buckley N. J., Poulton S. H. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alone and with chemotherapeutic agents. Effect on nude mouse-supported human bladder cancer heterografts. Arch Surg. 1989 Jan;124(1):107–110. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410010117023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSaia P. J., Sinkovics J. G., Rutledge F. N., Smith J. P. Cell-mediated immunity to human malignant cells. A brief review and further studies with two gynecologic tumors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Dec 1;114(7):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. Interstrand cross-links and sequence specificity in the reaction of cis-dichloro(ethylenediamine)platinum(II) with DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5027–5032. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. Reevaluation of interaction of cis-dichloro(ethylenediamine)platinum(II) with DNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3912–3915. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erusalimsky J. D., Friedberg I., Rozengurt E. Bombesin, diacylglycerols, and phorbol esters rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of an Mr = 80,000 protein kinase C substrate in permeabilized 3T3 cells. Effect of guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19188–19194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isonishi S., Andrews P. A., Howell S. B. Increased sensitivity to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) in human ovarian carcinoma cells in response to treatment with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3623–3627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. M., Hong W. S., Lee J. O., Kang T. W., Kim Y. W., Song J. K., Yun T. K., Kim C. Y. Enhancement of cytotoxicity of cisplatin in vitro by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor and/or recombinant human interferon-alpha, -beta and -gamma. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 Sep;80(9):904–909. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb01733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Brown D. C., Dinarello C. A. Growth-promoting effect of recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor for a human astrocytoma cell line. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2913–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S. T., Griffin D. B., Fiers W., Balkwill F. R. Paradoxical effects of tumour necrosis factor in experimental ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 1989 Nov 15;44(5):918–925. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S. T., Naylor M. S., East N., Oliff A., Balkwill F. R. Cells secreting tumour necrosis factor show enhanced metastasis in nude mice. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26(10):1031–1034. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90044-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. C., Andrews P. A., Howell S. B. Modulation of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) accumulation and sensitivity by forskolin and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine in sensitive and resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jul 30;48(6):866–872. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin B is a major bombesin-like peptide in rat brain: regional distribution of neuromedin B and neuromedin C in rat brain, pituitary and spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutch D. G., Powell C. B., Kao M. S., Collins J. L. In vitro analysis of the anticancer potential of tumor necrosis factor in combination with cisplatin. Gynecol Oncol. 1989 Sep;34(3):328–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(89)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor M. S., Malik S. T., Stamp G. W., Jobling T., Balkwill F. R. In situ detection of tumour necrosis factor in human ovarian cancer specimens. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26(10):1027–1030. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90043-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. V., Schrey M. P. Activation of inositol phospholipid signaling and Ca2+ efflux in human breast cancer cells by bombesin. Cancer Res. 1990 Jan 15;50(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J. Bombesin stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in cultures of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Nottrott S., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor signal transduction. Cell-type-specific activation and translocation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2604–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swope S. L., Schonbrunn A. The biphasic stimulation of insulin secretion by bombesin involves both cytosolic free calcium and protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):193–202. doi: 10.1042/bj2530193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Zuckerman J. E., Bostwick D. G., Bensch K. G., Sikic B. I., Raffin T. A. Gastrin releasing peptide is a selective mitogen for small cell lung carcinoma in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):306–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI111690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Rozengurt E. High-affinity receptors for peptides of the bombesin family in Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7616–7620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


