Figure 6.
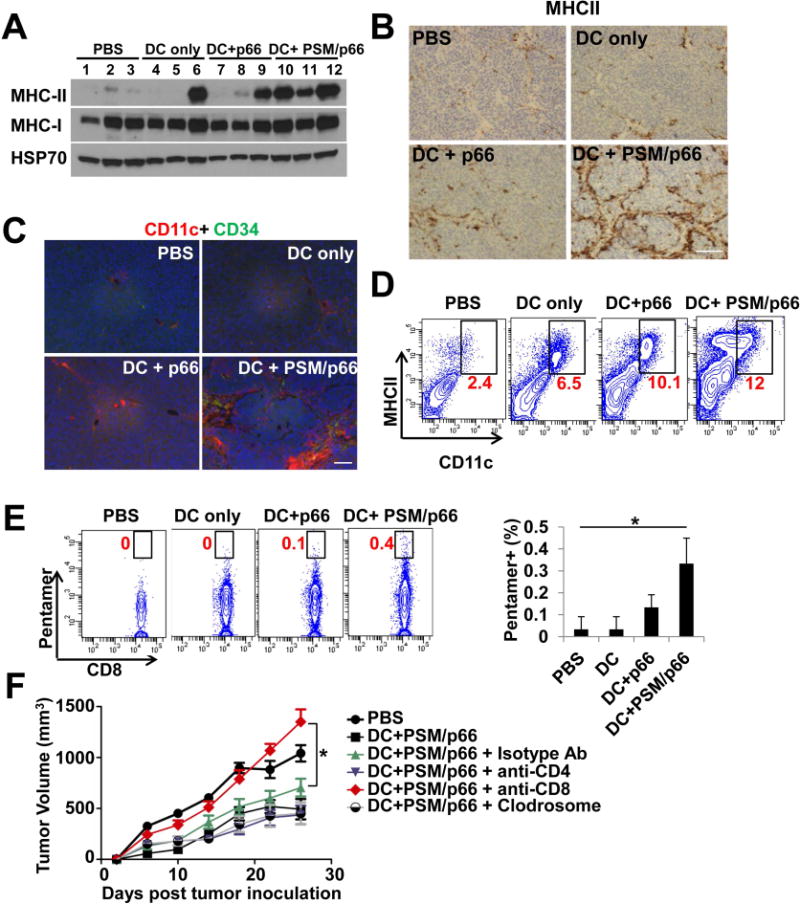
DCs primed with PSM/HER2 elicited CD8 T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity.
(A) Western blot analysis on MHCII protein levels in TUBO tumor tissues from post-treatment Balb/c mice. Tumor tissues were harvested 10 days after treatment.
(B) Immunohistochemical staining of MHCII in TUBO tumor tissues from post-treatment Balb/c mice. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(C) Immunofluorescent staining of CD11c and CD34 (vascular marker) in TUBO tumor tissues from post-treatment Balb/c mice. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(D) Flow cytometry analysis on CD11c- and MHCII-double positive cells isolated from post-treatment TUBO tumor tissues. Percentage of CD11c- and MHCII-double positive cells in each sample was labeled in red.
(E) Enhanced HER2-specific CD8 T cells in post-treatment TUBO tumors. Left: Flow cytometry analysis on CD8 and p66-pentamer positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in post-treatment tumor tissues. Right: Quantification of percentage of p66-pentamer positive CD8 T cells in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
(F) Effect of immune cell depletion on inhibition of TUBO tumor growth by DC+PSM/p66 treatment. Balb/c mice inoculated with TUBO tumor (n = 8/group) were treated with a control isotype antibody, anti-CD4 antibody, anti-CD8 antibody, or clodrosome to deplete specific cell types. Mice were then treated with DC+PSM/p66, and tumor growth was monitored in the next 4 weeks. Tumor volume is presented as mean ± SEM.
Data are represented as mean ± S.D. except tumor volume. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01.
