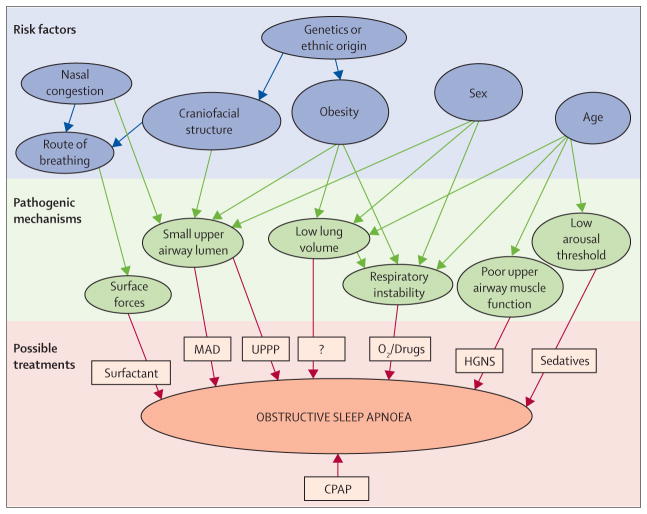
Figure 1. Risk factors, pathogenic mechanisms, and treatments for obstructive sleep apnoea.
Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea have long been recognised, but novel pathogenic mechanisms have now been detected in patients with the disorder. Although CPAP is the current treatment of choice irrespective of underlying cause, treatments based on tackling individual pathogenic mechanisms might prove a successful alternative approach in the future. CPAP=continuous positive airway pressure. MAD=mandibular advancement device. UPPP=uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. HGNS=hypoglossal nerve stimulation. Figure adapted from Jordan and colleagues,16 by permission of Elsevier.