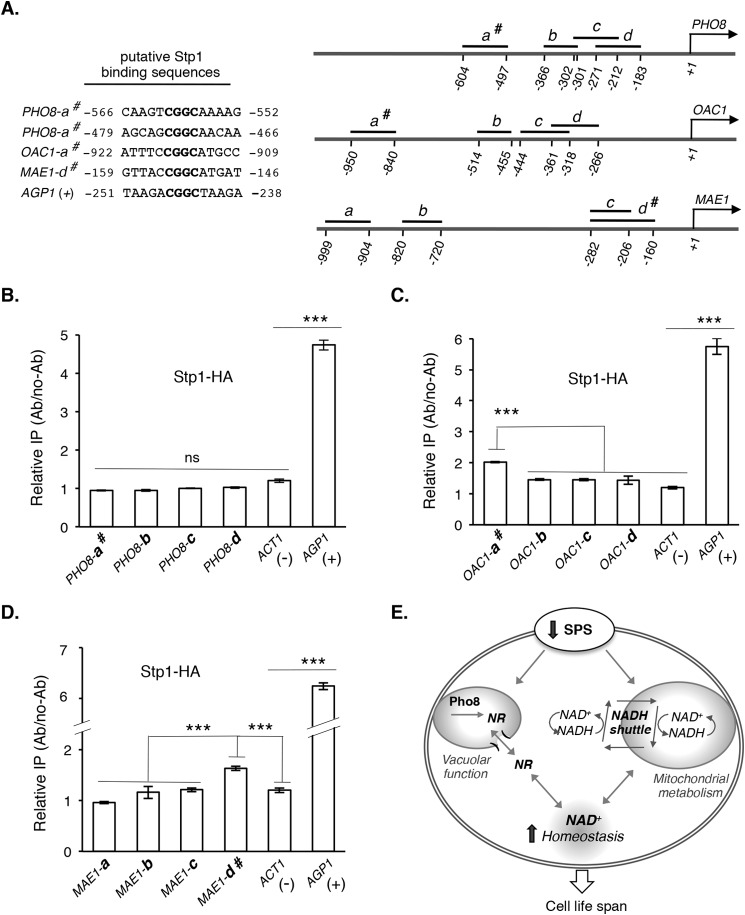
FIGURE 5.
Stp1, a transcription factor of SPS signaling pathway, may directly bind to the promoter regions of NADH shuttle components. A, putative binding sites of Stp1 in the promoter regions of PHO8, OAC1, and MAE1 are shown in the left panel. DNA fragments used for ChIP analysis are shown in the right panel. # denotes fragments containing a putative Stp1 binding site. B, HA-tagged Stp1 (Stp1-HA) does not significantly bind to various promoter regions of PHO8 compared with AGP1 as positive control (+) and ACT1 as negative control (−), determined by qPCR. C, Stp1-HA significantly binds to OAC1-a# but not other promoter regions of OAC1. D, Stp1-HA significantly binds to MAE1-d# but not other promoter regions of MAE1. E, proposed model of how reduced SPS signaling leads to increased NAD+ homeostasis (via NR salvage and NADH shuttle), which works in concert with mitochondrial and vacuolar metabolism to maintain cell function and extend life span. For clarity, additional factors and interactions are not shown. Data shown are representative of multiple independent experiments. Error bars denote S.D. derived from triplicate samples. The p values were calculated using Student's t test (ns, not significant; ***, p < 0.005).