FIGURE 3.
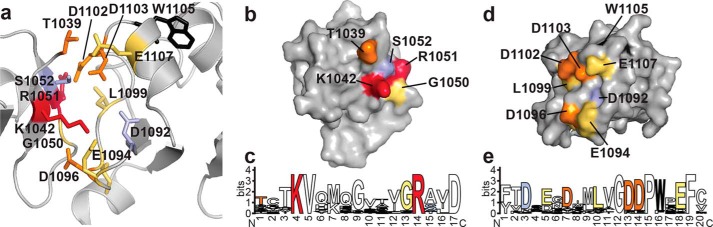
Binding contributions of ARF7 PB1 domain interface residues. a, structure of the ARF7 PB1 domain interface. The view shows the interface between two ARF7 PB1 domains (Ref. 13; PDB code 4NJ6). Residues contributed by the basic face of one PB1 domain (left) and by the OPCA face of a second PB1 domain (right) are shown as stick models. Colors correspond to the effect of alanine mutations on Kd determined by ITC experiments, as follows: light purple, <2-fold; yellow, 2–10-fold; orange, >10-fold. Residues that abolished detectable interactions are red. The structurally important tryptophan is black. The same color scheme is used in panels b–e. b, surface representation of the ARF7 PB1 domain basic face. Positions of residues with colors corresponding to changes in binding affinity are indicated. c, amino acid sequence logo showing conservation of residues on the ARF7 PB1 domain basic face of all 22 Arabidopsis ARF proteins. d, surface representation of the ARF7 PB1 domain OPCA face. Positions of residues with colors corresponding to changes in binding affinity are indicated. e, amino acid sequence logo showing conservation of residues on the ARF7 PB1 domain OPCA face of all 22 Arabidopsis ARF proteins. Panels c and e were generated using WebLogo (39).
