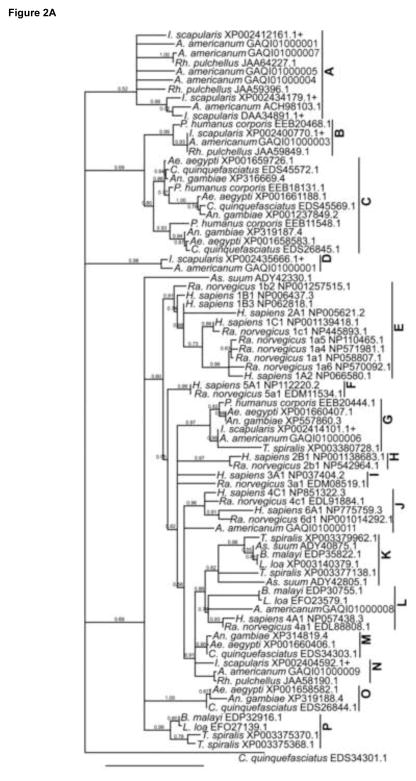
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic analyses based on extracellular loop 5 and transmembrane domains 8 and 10: (A) Ixodes scapularis organic anion transporting polypeptides and those from Rhipicephalus pulchellus and Amblyomma americanum ticks, human, rat, and other bloodsucking arthropods, blood- and tissue-dwelling parasites were used to construct phylogenetic tree. Ixodes scapularis sequences are marked with a plus sign. (B–D) Amino acid sequence alignment of tick Oatp orthologs from clusters B, D, and N. Conserved amino acids are highlighted in gray.