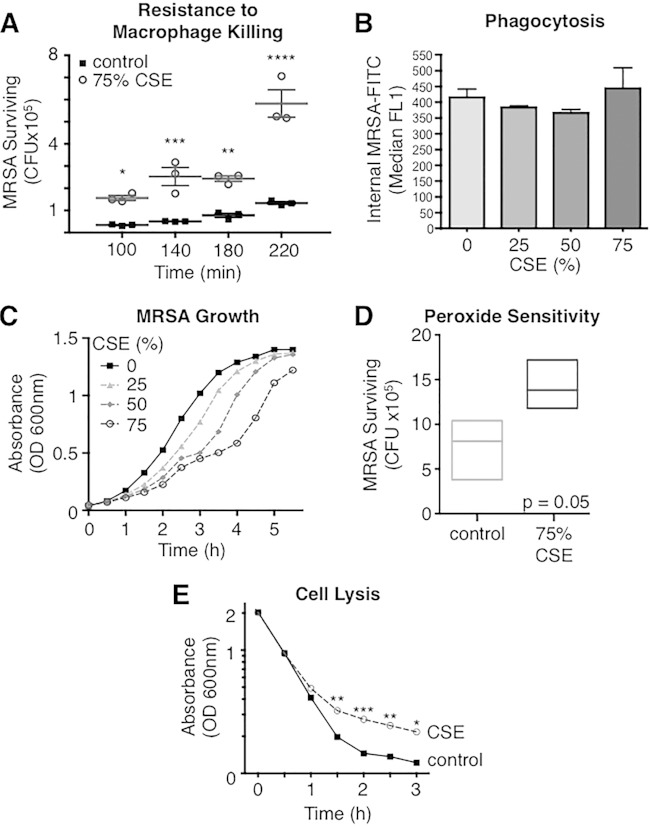
FIG 1.
Cigarette smoke exposure reduces MRSA susceptibility to macrophage killing and lysis while suppressing bacterial growth. (A) Starting with an MOI of 1 × 105, control MRSA was killed by alveolar macrophages over 100 min, while MRSA exposed to 75% CSE resisted killing and overgrew. By 220 min, CFU of control MRSA were 4-fold lower than those of CSE-MRSA. (B) CSE exposure did not change the rate of MRSA-GFP phagocytosis by macrophages. (C) The increased numbers of MRSA during killing assays was not due to increased growth, as CSE decreased the rate of MRSA growth in a dose-dependent manner. (D) CSE exposure tended to increase MRSA resistance to killing by H2O2 (oxygen radicals). (E) CSE induced resistance to MRSA cell lysis in the presence of detergent. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.