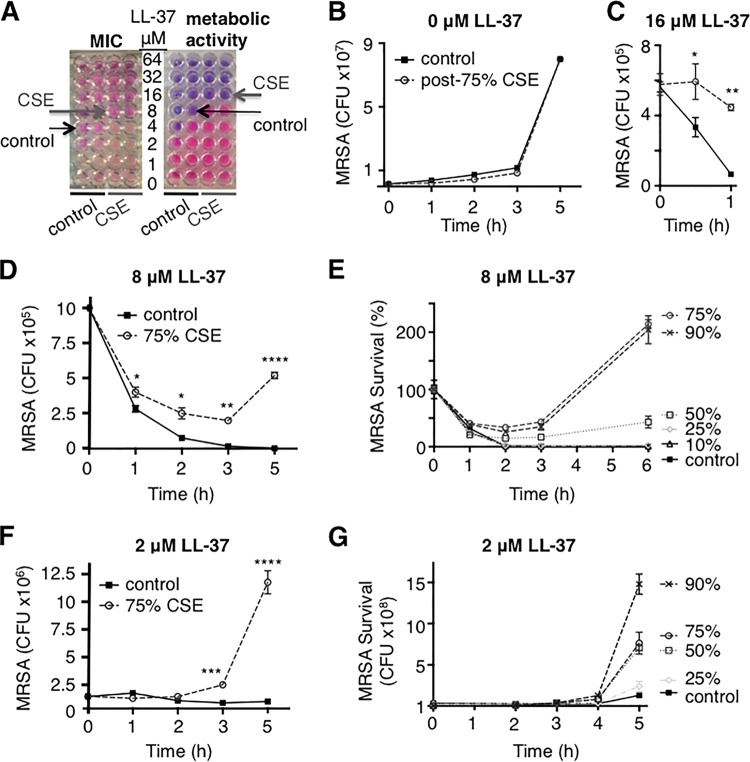
FIG 2.
Cigarette smoke exposure increases resistance of MRSA to human AMP LL-37. (A) CSE exposure increased the MIC of MRSA to LL-37 from 4 to 8 μM and increased the concentration needed to inhibit metabolic activity from 8 to 16 μM. (B) Growth of control MRSA and MRSA after exposure to 75% CSE was identical during the AMP growth kinetics assays, which were run without CSE present. (C, D, and F) Prior exposure to 75% CSE allowed MRSA to escape killing by LL-37 at 16 μM (C), 8 μM (D), and 2 μM (F). (E and G) These effects were CSE dose dependent, with exposure to 50% through 90% CSE inducing resistance to AMP killing at both 8 μM (E) and 2 μM (G). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.