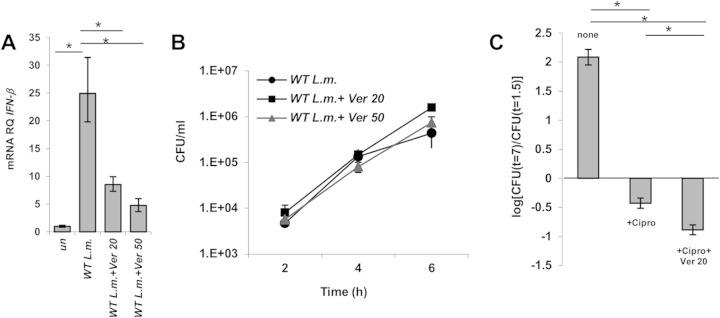
FIG 2.
Verapamil inhibits P-gp and leads to a reduced IFN-β response in infected THP-1 cells. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of IFN-β transcription levels in THP-1 cells infected with wild-type L. monocytogenes supplemented with 20 μM or 50 μM verapamil (Ver 20 and Ver 50, respectively). Transcription levels are represented as RQs relative to uninfected cells. An experiment representative of 3 independent repeats is shown. The error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. (B) Intracellular growth curves of WT L. monocytogenes in THP-1 cells supplemented with 20 or 50 μM verapamil. Representative growth curves from 3 independent experiments are shown. The error bars represent standard deviations of triplicates. (C) Intracellular bacterial counts of THP-1 cells infected with wild-type L. monocytogenes and supplemented as indicated with 4.5 μM ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and 20 μM verapamil. An experiment representative of 3 independent repeats is shown. The error bars represent standard deviations of triplicates. *, P < 0.05.