Figure 6.
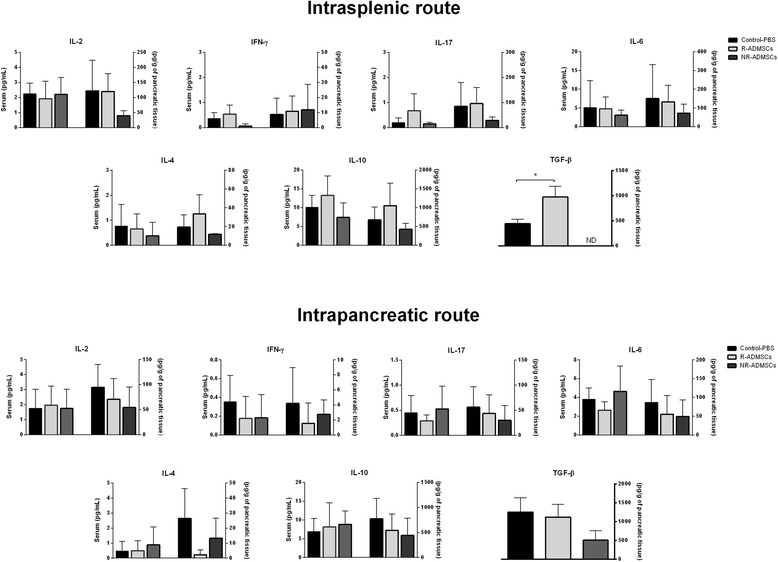
Intrasplenic adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell administration increases transforming growth factor beta levels in pancreatic tissue of diabetic treated mice. Blood and pancreas samples were obtained from Control and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell (ADMSC)-treated mice 70 days after treatment. The pancreatic tissue was weighed and homogenized in the presence of proteases inhibitor. Levels of interleukin (IL)-2, interferon gamma (IFN-γ), IL-17, IL-6, IL-4 and IL-10 were measured in serum and pancreatic homogenate using the cytokine bead array (CBA) method. The transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) level was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay only in pancreatic tissue samples. Serum cytokine concentrations are represented by picograms of protein per milliliter (left y axis) and pancreatic cytokine concentrations are represented by picograms of protein per gram of pancreatic tissue (right y axis). Bars represent average ± standard error of the mean. Intrasplenic route: Control-PBS, n = 5; R-ADMSCs, n = 7; NR-ADMSCs, n = 3. Intrapancreatic route: Control-PBS, n = 5; R-ADMSCs, n = 5; NR-ADMSCs, n = 7. *P <0.05 (Control-PBS vs. R-ADMSCs). ND, not detected; NR-ADMSCs, nonresponder ADMSC-treated mice; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; R-ADMSCs, responder ADMSC-treated mice.
