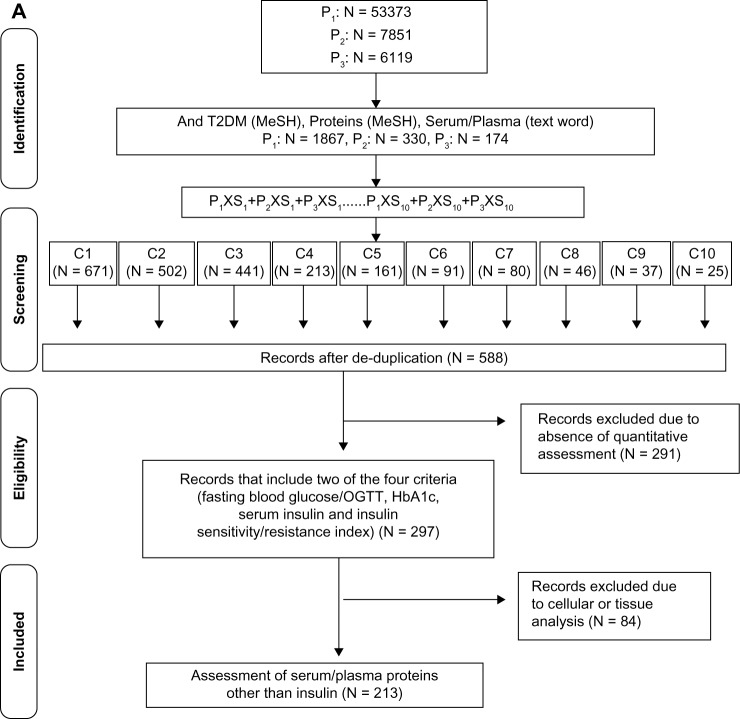
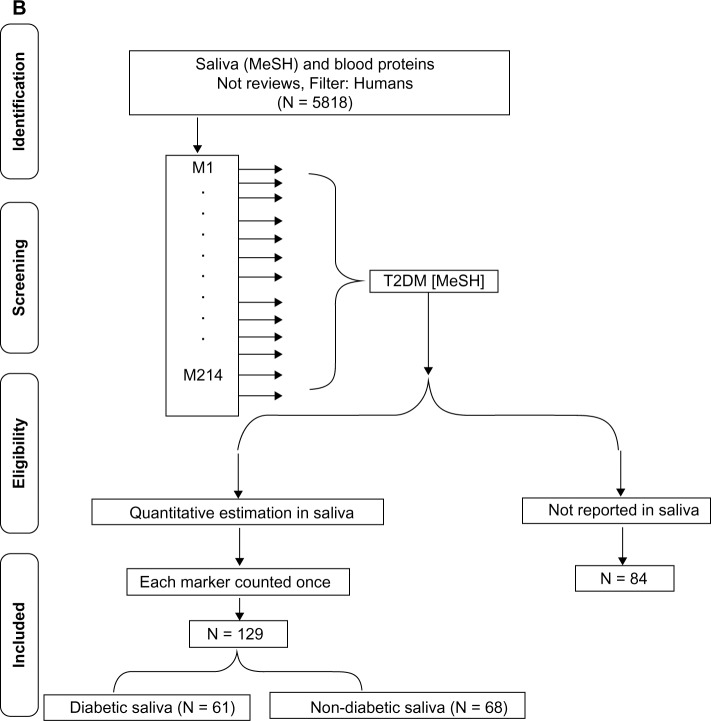
Figure 1.
T2DM-specific circulating protein markers. (A) Literature-based search of the PubMed database for identifying T2DM-specific serum proteins using the MeSH terms insulin resistance (P1) or glucose intolerance (P2), or insulin secreting cells (P3) and each of the 10 secondary sets is shown. [S1: lipids/blood, S2: obesity, S3: adipokines, S4: antibodies and globulins, S5: glycoproteins, S6: blood, coagulation factors, S7: inflammation mediators, S8: oxidative stress, S9: endothelium, and S10: iron-binding proteins]. The S1–10 × (P1 + P2 + P3) constitute the 10 common sets C1–C10. (B) Flow diagram of the search strategy for identification of T2DM-associated circulating protein biomarkers reported in saliva. The PubMed database was searched for saliva (MeSH) and blood proteins, the cohort being filtered for humans and English language. The articles in the retrieved cohort were searched for circulating biomarkers identified in (A) and manually screened for quantitation in saliva. The publication cohort of T2DM-specific circulating protein biomarkers reported in saliva was further divided into two groups based on articles reporting quantitation in T2DM saliva (diabetic saliva) or other conditions (nondiabetic saliva).