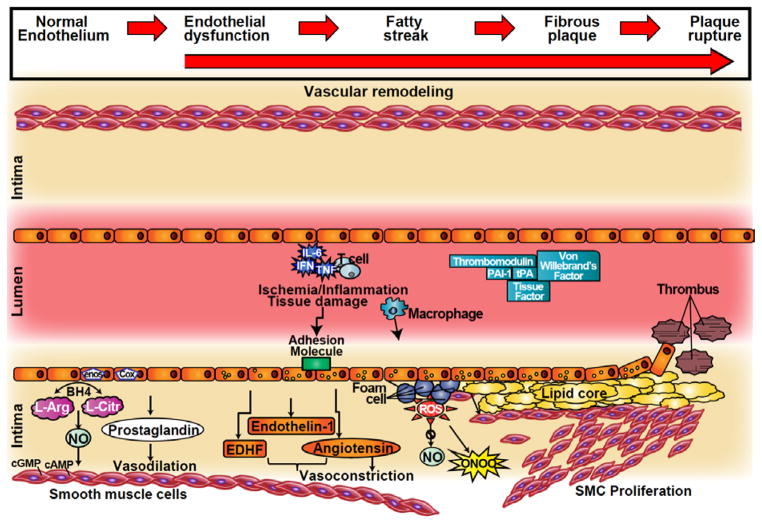
Figure 1.
Cross-sectional depiction of a coronary artery progressing from normal endothelial function to endothelial dysfunction and plaque formation (left to right). In the healthy state the endothelium is responsible for regulating vascular tone with balanced production of vasodilators and vasoconstrictors. In endothelial dysfunction this balance is disrupted in favor of the vasoconstrictors. An inflammatory and/or pro-thrombotic state promotes the formation of the plaque, plaque erosion and rupture.
cGMP = cyclic guanosine monophosphate; cAMP = cyclic adenosine monophosphate; NO = nitric oxide; NOS = nitric oxide synthase; COX = cyclooxygenase; BH4 = tetrahydrobiopterin; L-arg = L-arginine; L-cit = L-citrulline; EDHF= endothelium derived hyperpolarizing factor; IL = interleukin; TNF = tumor necrosis factor; ONOO = peroxinitrite; PAI1= plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; tPA = tissue plasminogen activator; ROS = reactive oxygen species; SMC = Smooth muscle cells