Figure 1.
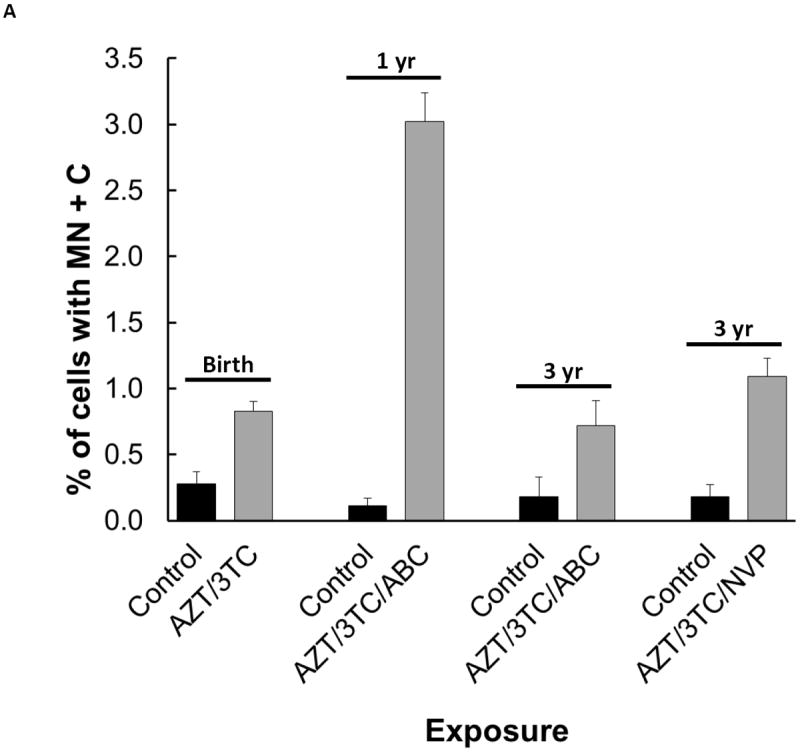
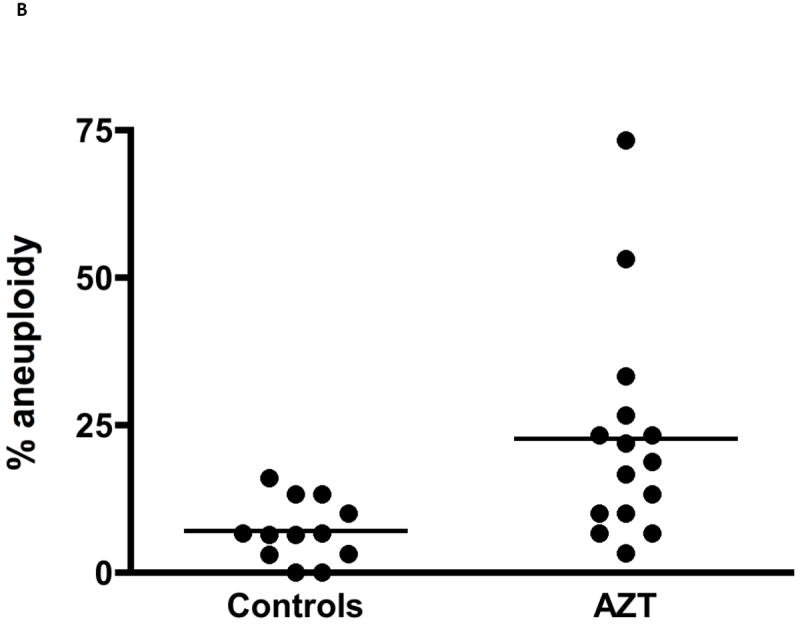
Aneuploidy observed as: (A) MN+C in cultured bone marrow cells from patas monkey offspring; and (B) percentage of human cord blood CD34(-) cells with aneuploidy by karyotype analysis of metaphase spreads. For (A), a graph using the data in [16], pregnant patas dams were given human-equivalent daily doses of ARV drugs, or no drugs, for the last 50% (10 wk) of gestation. Bone marrow cells, obtained from the offspring at birth (AZT/3TC), 1 yr of age (AZT/3TC/ABC) and 3 yr of age (AZT/3TC/ABC or AZT/3TC/NVP) were cultured and stained with: DAPI to reveal MN; and CREST antiserum to reveal centromeres within the MN. The Figure shows % of cells with MN+C (2-4 monkeys/group, 5000 cells/monkey), where control vs. NRTI-treated p values were ≤ 0.05 for each treatment. For (B), taken from [17], cord blood CD34(-) cells were obtained from 15 AZT-exposed pregnancies and 12 uninfected pregnancies, PHA-stimulated, cultured for 72 hr and karyotyped. The % of cells with aneuploidy, based on 30 metaphases from each individual, was significantly higher in the AZT-exposed group than in the unexposed group (p≤ 0.001).
