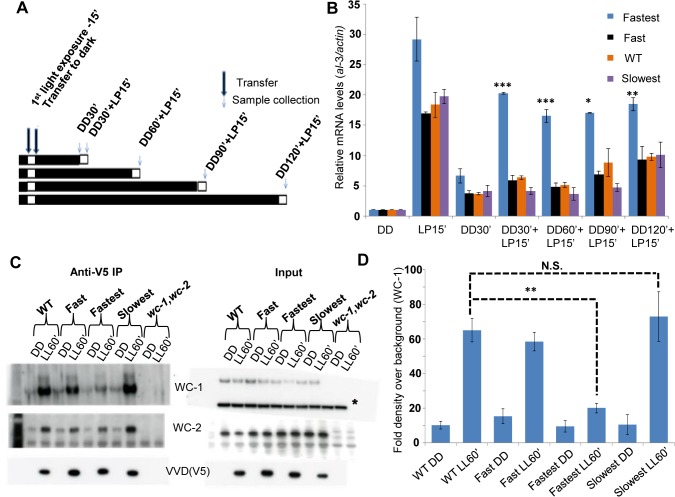
Fig 3. The fastest photocycle mutant is unable to inhibit White Collar Complex (WCC) activity due to reduced VVD-WCC interaction.
(A) Two-pulse experimental design for testing WCC transcriptional activity in response to a second light pulse. Strains (n = 3) were exposed to a 15 minute white light pulse (LP15’, 40 μM m-2s-1) resulting in the induction of VVD then followed by dark transfer (DD) and a subsequent 15 minute light pulse (LP15’, 40 μM m-2s-1) after various times in the dark (DD30’,DD60’, DD90’, DD120’). (B) WCC activity after second light pulse as determined by al-3 gene expression shows that the fastest photocycle mutant is able to reactivate WCC to a greater extent when compared to WT and other mutants. (C) VVD-WCC interaction using DSP cross-linking under white light (40 μM m-2s-1) conditions [25]. VVD-V5 co-IP pull down products (WCC and VVD) were analyzed using Western Blotting techniques. Membranes for Anti-V5 IP were developed using more sensitive Femto reagent and the wc-1,wc-2 null strain was used as a background control for the Western Blots. (D) Blots (n = 3) were quantified by densitometry using NIH Image J software to measure VVD-WCC interaction in the WT and mutants. * non-specific band/ loading control on Western blots. Asterisks indicate statistical significance when compared with WT as determined by an unpaired t test. ***P < 0.001, **P<0.01 *P<0.05, N.S.- difference not significant.