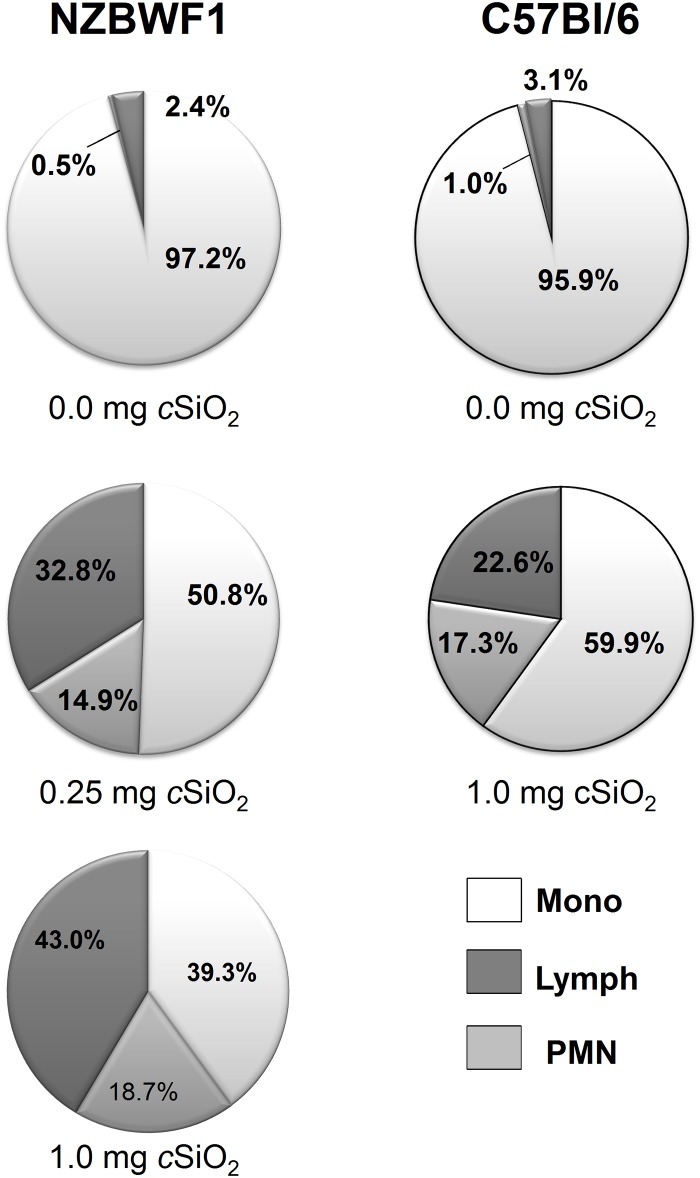
Fig 8. Intranasal cSiO2 exposure induces infiltration of lymphocytes and PMN leukocytes in BALF of NZBWF1 and C57Bl/6 mice.
Cytometric slides prepared from BALF were stained with Diff-Quick and 200 cells per slide identified as monocytes/macrophages (Mo), lymphocytes (Lymph) or polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells. In NZBWF1 mice, group mean ± SEM at 0.0 mg cSiO2 were 97.2 ± 0.4%, 2.4 ± 0.3%, and 0.5 ± 0.1% for Mo, Lymph and PMN, respectively. Group mean ± SEM for 0.25 mg cSiO2 group were 50.8 ± 2.9%, 32.8 ± 3.5%, and 14.0 ± 1.8%, respectively and for the 1.0 mg cSiO2 group were 39.3 ± 1.7%, 43.0 ± 2.5%, and 18.7 ± 1.8%, respectively. In C57Bl/6 mice, group mean ± SEM at 0.0 mg cSiO2 were 95.9 ± 0.9%, 3.1 ± 0.7% and 1.0 ± 0.2% for Mo, Lymph, and PMN, respectively. Group mean ± SEM for 1.0mg cSiO2 were 59.9 ± 3.7%, 22.6 ± 3.7, and 17.3 ± 2.1% for Mo, Lymph, and PMN, respectively.