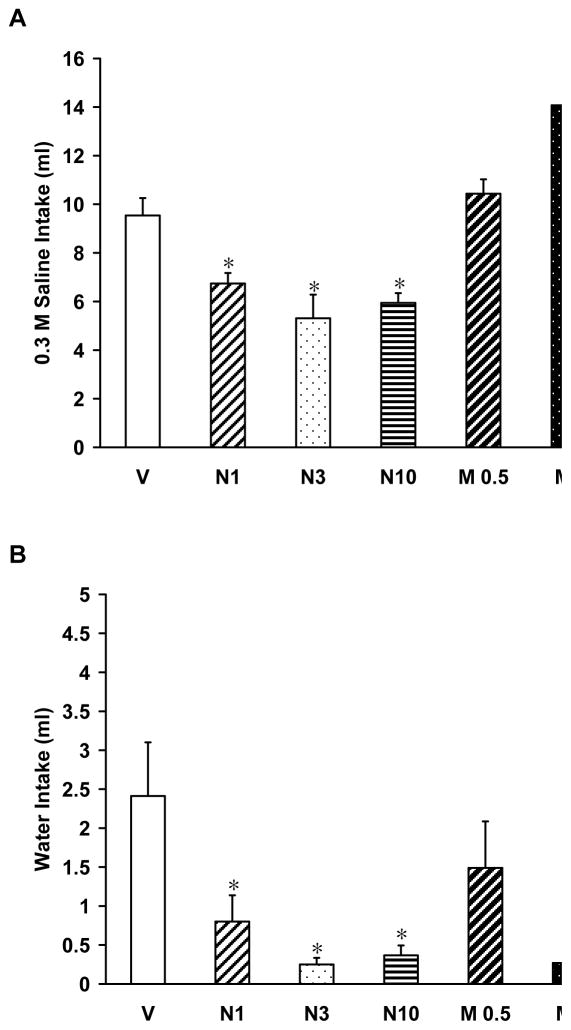
Figure 1.
Mean (± SEM) water and 0.3 M saline intakes in rats given naltrexone or morphine after furosemide-induced sodium depletion. (A) Rats given naltrexone drank significantly less 0.3 M saline than vehicle and morphine treated rats. Rats given the two highest doses of morphine (M1 and M3) drank significantly more 0.3 M saline than vehicle and naltrexone treated rats. (B) Water intake was significantly affected by acute treatment with naltrexone or morphine. Rats given naltrexone and the two highest doses of morphine decreased water intake during the 2 h test. * p<0.05 compared to vehicle group