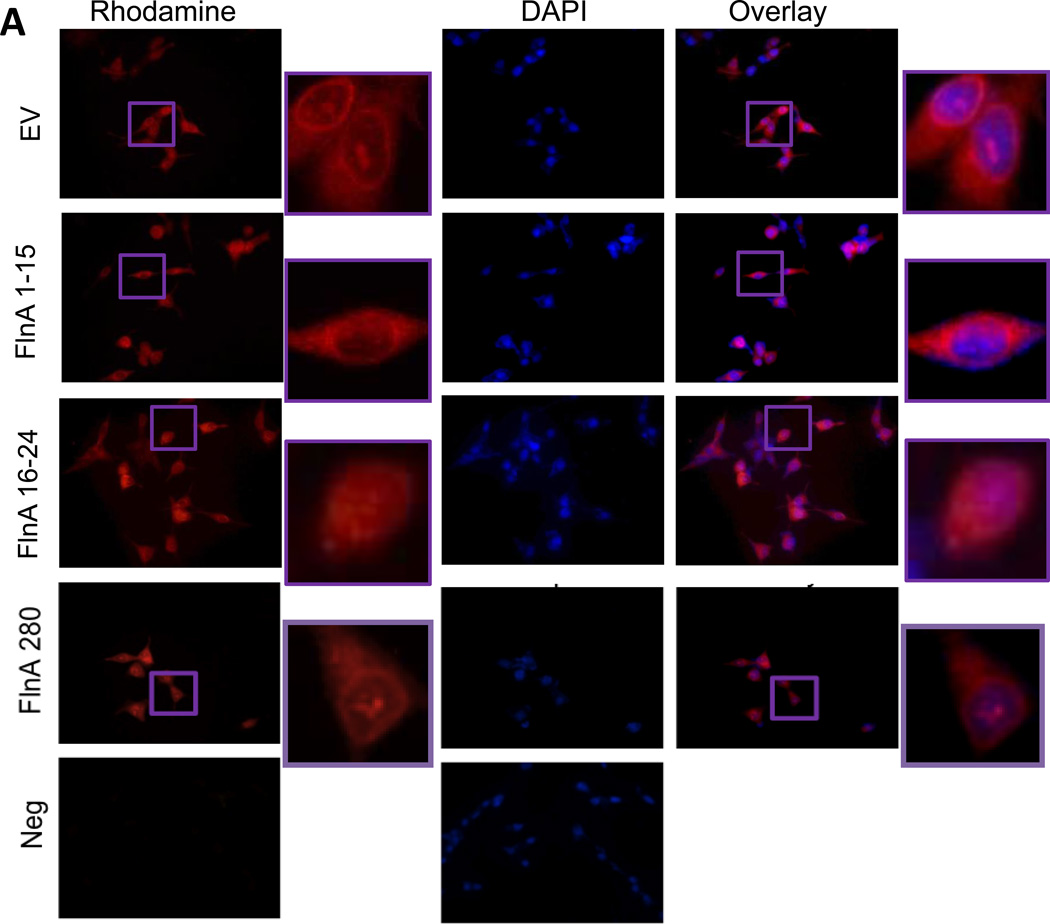
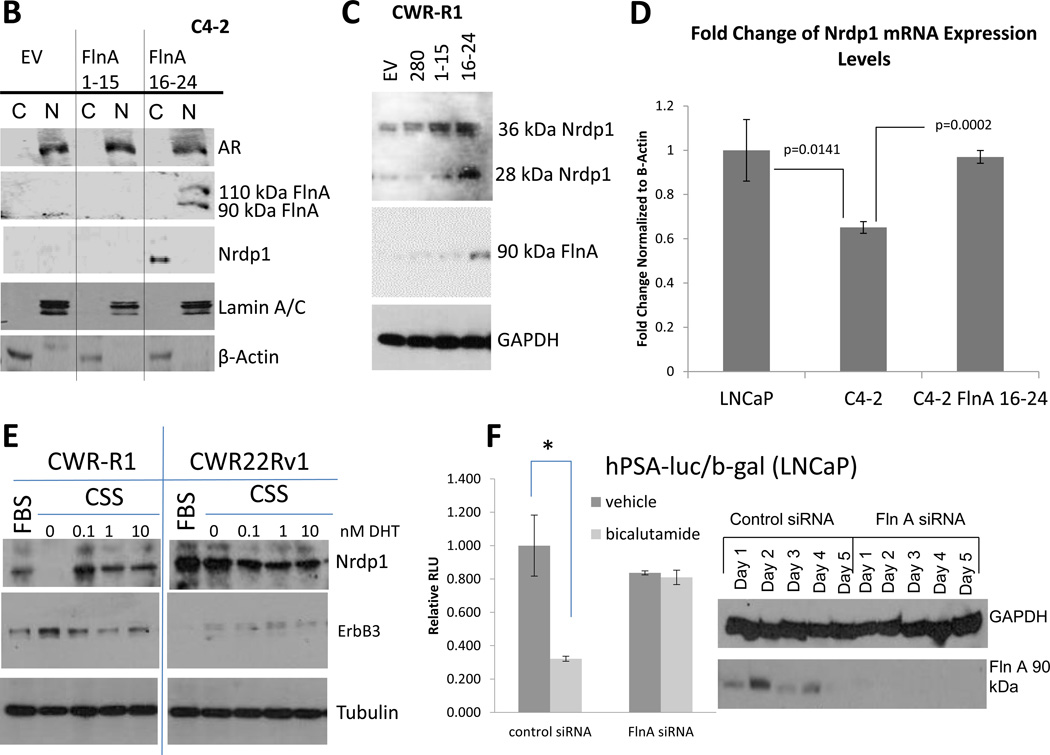
Figure 6. The 90kDa FlnA isoform localized to the nucleus and promoted apoptosis and growth arrest in a ligand dependent manner.
(A) Immunofluorescence of C4-2B cells transfected with empty vector (EV), FlnA 1-15, or FlnA 16-24. Cells were stained for C-terminal FlnA or DAPI to identify the location of the nucleus. (top panel) Control cells (transfected with empty vector) only express cytoplasmic FlnA, as demonstrated by unstained nuclear regions in FlnA stained cells, (2nd panel) and transfection of FlnA 1-15 did not affect the localization, (3rd panel) while those transfected with FlnA 16-24 express both cytoplasmic and nuclear FlnA. (4th panel) Transfection of full-length FlnA did not restore nuclear localization completely. (5th panel) Negative controls were treated the same but did not use the anti-FlnA antibody (bar=30µm). (B) Subcellular fractionation of C4-2 cells transfected with empty vector, FlnA 1-15, or FlnA 16-24. Fractionated cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-Nrdp1, anti-AR, anti-FlnA (C-terminal), anti-β-Actin (to demonstrate specificity of cytoplasmic fraction), and anti-Lamin A/C (to demonstrate specificity of nuclear fraction) and demonstrates that transfection of FlnA 16-24 caused nuclear expression of FlnA and restores Nrdp1 protein in C4-2 cells, although AR levels were not altered. (C) Protein expression of Nrdp1 in CWR-R1 cells is regulated by the 90 kDa FlnA. Whole cell lysates of CWR-R1 cells that were transfected with empty vector, full length FlnA, FlnA 1-15, or FlnA 16-24 were immunoblotted with anti-FlnA, anti-Nrdp1, and anti-tubulin antibodies. Nrdp1 protein levels increased with the increased levels of the 90 kDa FlnA fragment. (D) FlnA restores Nrdp1 expression in CRPC cells. qPCR for Nrdp1 expression in LNCaP, C4-2, and stably transfected C4-2-FlnA(16-24) showed that Nrdp1 expression was reduced in C4-2 compared to LNCaP cells (p=0.0141), but expression of FlnA16-24 in C4-2 cells restored Nrdp1 expression to a level similar to LNCaP cells (p=0.0002 compared to C4-2). Nrdp1 transcript levels were normalized to the corresponding values for β-Actin. (E) Comparison of Nrdp1 response to changes in AR in CWR-R1 and CWR22-Rv1 cells cultured in FBS, CSS or CSS treated with increasing doses of DHT as indicated. Lysates were immunoblotted with anti-Nrdp1, anti-ErbB3, and anti-tubulin antibodies. While the levels of Nrdp1 in CWR22Rv1 cells were unaltered despite culture in CSS, in CWR-R1 these levels altered slightly. (F) (left) Reporter gene activity of AR on a luciferase-tagged PSA promoter section demonstrates that in control LNCaP cells, 10 µM bicalutamide is able to suppress AR activity whereas in cells where FlnA is downregulated by siRNA, bicalutamide failed to affect AR activity. (right) Western blotting demonstrating the efficacy of FlnA siRNA used.