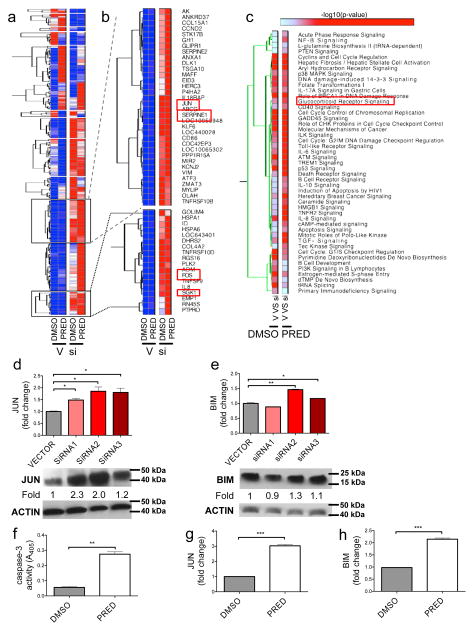
Figure 5. BALR-2 plays a role in the glucocorticoid response pathway.
(A) Hierarchical gene clustering of microarray data from RS4;11 cells treated with or without siRNA2 against BALR-2 and with or without prednisolone. Abbreviations, V, Vector; si, siRNA 2 against BALR-2; DMSO, Dimethylsulfoxide (used to solubilize prednisolone); PRED, prednisolone. (B) Two clusters of genes significantly over-expressed in siRNA2 treated cells include genes involved in glucocorticoid response (FOS, JUN, SGK1 and SERPINE1) (C) Functional analysis of genes differentially expressed in siRNA2 treated cells shows significant enrichment of various canonical pathways, including Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling. (D–E) RT-qPCR (top panels), showing upregulation of JUN (D), and BIM (E) in multiple siRNA knockdown lines, normalized to ACTIN, with corresponding Western blot (bottom panels). Fold change values are as quantitated by ImageJ and normalized to ACTIN. (F–H) Prednisolone treatment of RS4;11 cells resulted in induction of apoptosis, as measured by Caspase-3 activity (F) and upregulation of JUN (G) of BIM (H), as measured by RT-qPCR, normalized to ACTIN. Overall, the effects of the siRNA are similar to those induced by prednisolone treatment. Comparisons made using a two-tailed T-test, p<0.05 (*); p<0.005 (**); p<0.0005 (***).