Figure 4.
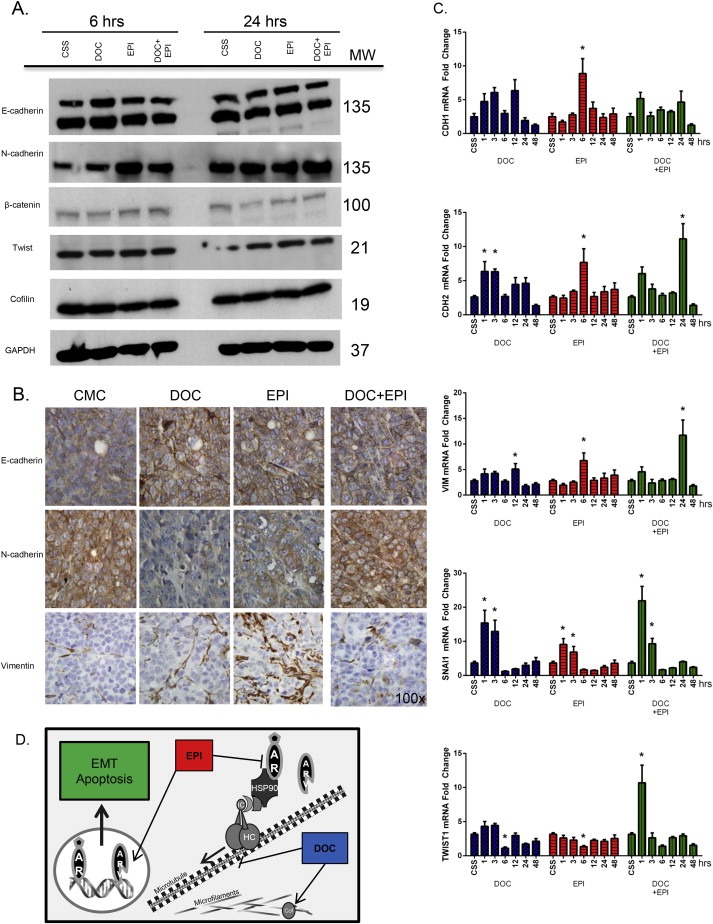
Impact of AR Variant on EMT in CRPC 22Rv1 Cells in Response to Combination Targeting of the AR NTD and Microtubules. Panel A, Western blot analysis of critical EMT regulator proteins after 6 and 24 h of treatment of 22Rv1 cells with DOC, EPI or combination. Expression levels for E‐cadherin, N‐cadherin, β‐catenin, Twist and the actin organization protein, cofilin are shown. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The MW of individual proteins is shown on the right (kDa). Panel B, serial sections of 22Rv1 prostate tumor xenografts from untreated control (CMC) and treated tumor‐bearing mice (DOC, EPI, or combination, obtained as in Fig.1B), were subjected to immunohistochemical analysis for the EMT markers E‐cadherin, N‐cadherin and vimentin. Magnification 100×. Panel C reveals the temporal analysis of gene expression of EMT regulators. 22Rv1 prostate cancer cells were treated with DOC, EPI or the combination (1, 3, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h) and mRNA expression was analyzed by RT‐PCR. The gene expression profile of mRNA for the EMT effectors, E‐cadherin (CDH1), N‐cadherin (CDH2), and vimentin (VIM), as well as for the transcriptional regulators SNAIL1 and Twist, in response to treatments is shown. Values represent the mean ± SEM of duplicate measurements from three independent experiments; (*) denotes statistical significance at p < 0.05. Panel D, schematic diagram projecting the potential interactions of AR with cytoplasmic proteins (dynein, tubulin, cofilin) that may control its nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity of target genes, mediating EMT and apoptosis in CRPC cells.
