Figure 1.
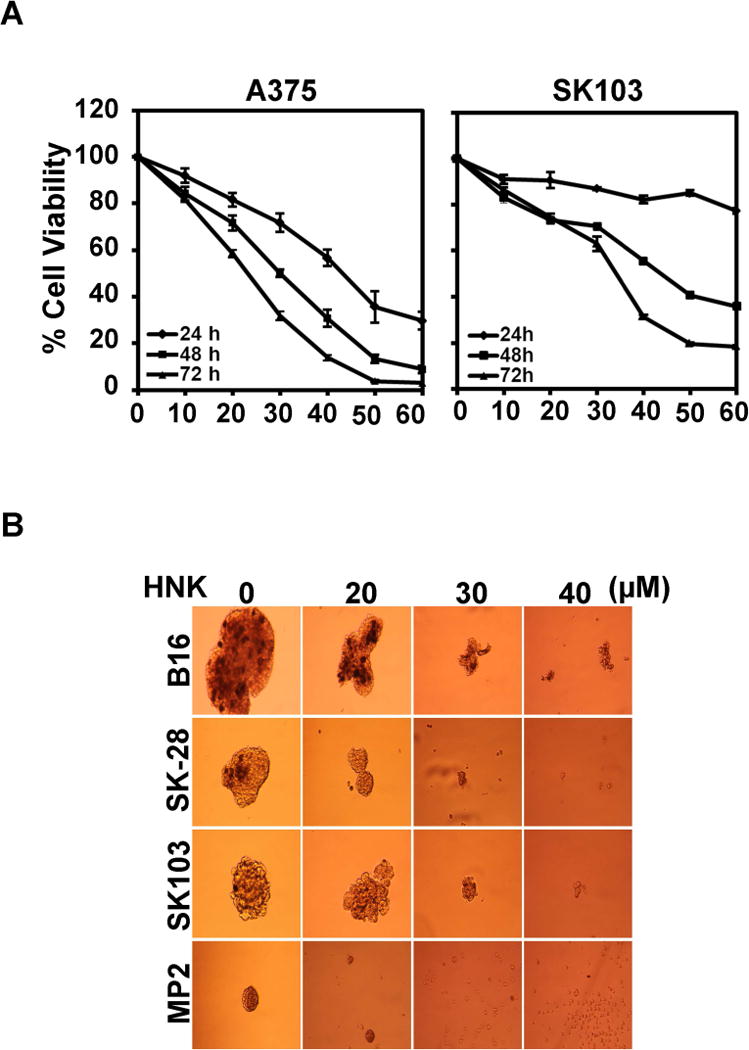
Honokiol inhibits growth and stemness of melanoma cells. (a) Cell proliferation assay showed HNK induced growth inhibitory effects on melanoma cells. Melanoma cells used in this study were incubated with increasing doses of HNK (0–60 μM) and cell viability was determined after 24, 48 and 72 h of HNK treatment. The experiments were conducted in quadruplicates, and repeated at least twice. The data were analyzed as percent of control, where the control wells were treated with equivalent amounts of DMSO alone. HNK resulted in a significant dose and time-dependent decrease in cell viability of B16/F-10, SKMEL-28, A375 and SK103 cells compared to their respective controls (P < 0.05). The results for the latter two cell lines are shown (b) HNK affects melanoma stem cells. For the melanosphere formation assay, cells were grown in ultralow attachment plates and treated with increasing concentrations of HNK (0–50 μM). After 7 days, the spheroids were photographed. HNK treatment significantly inhibited melanosphere formation in 3D culture (*p<0.05) in a dose dependent manner.
