Abstract
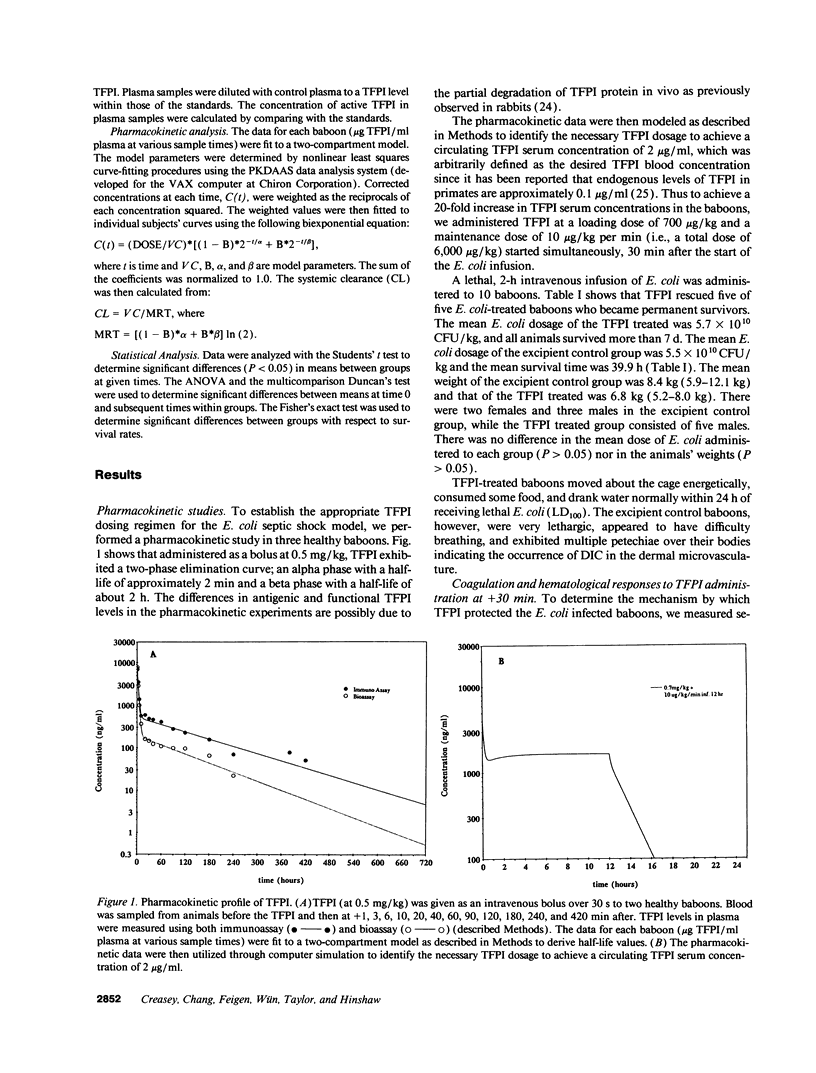
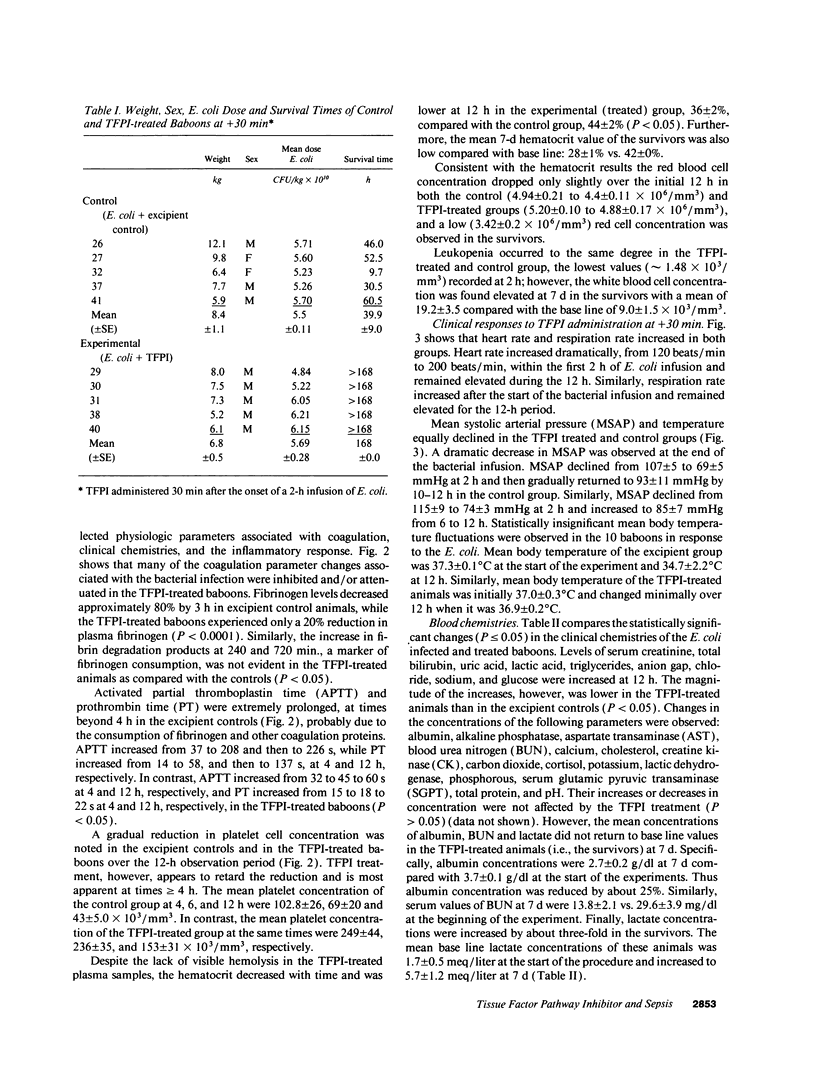
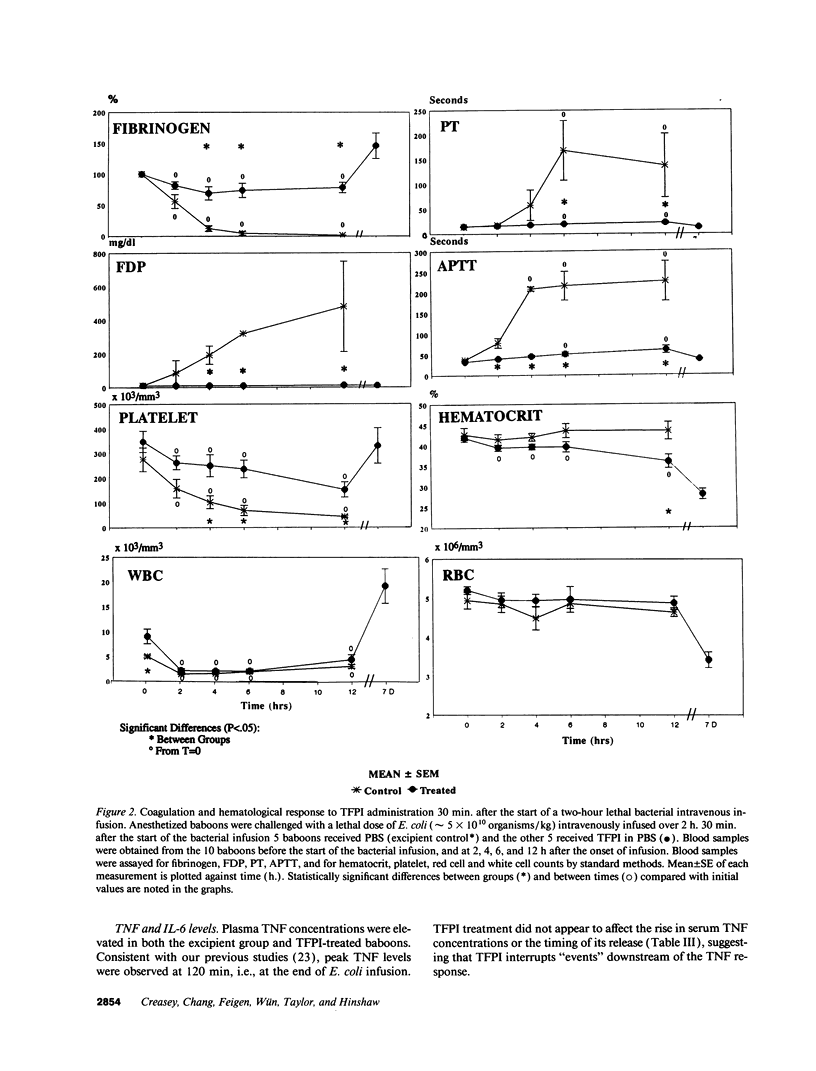
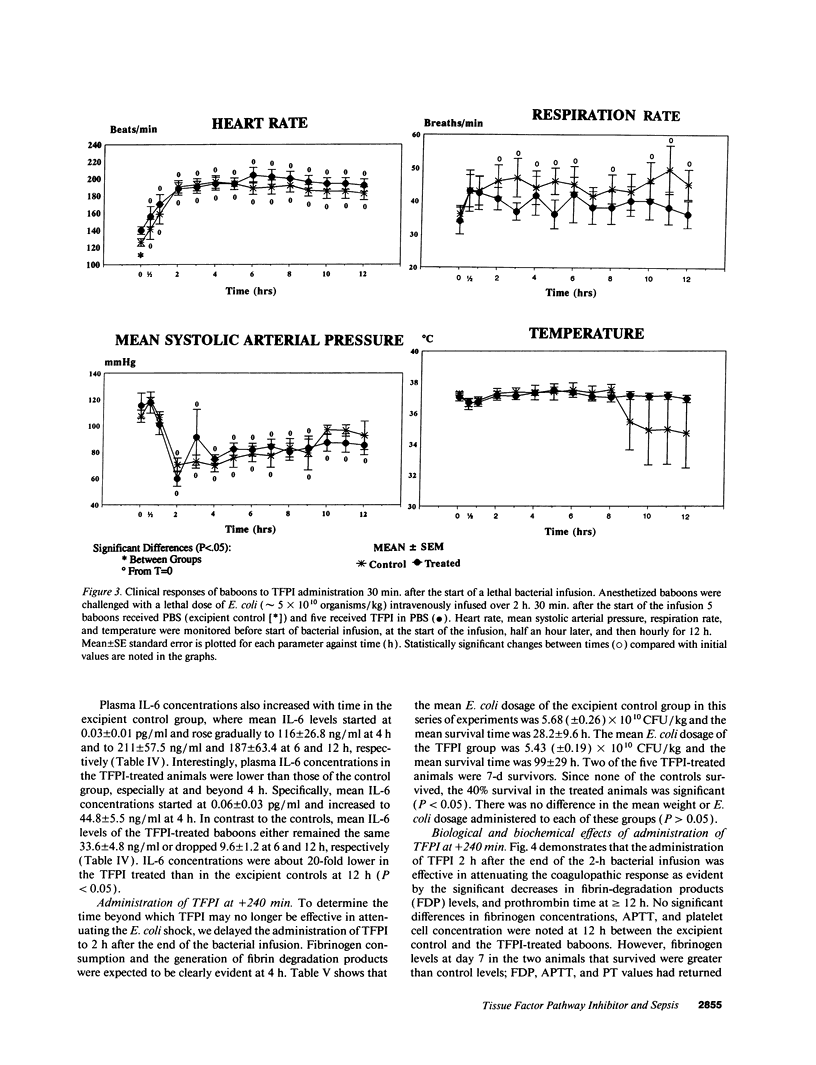
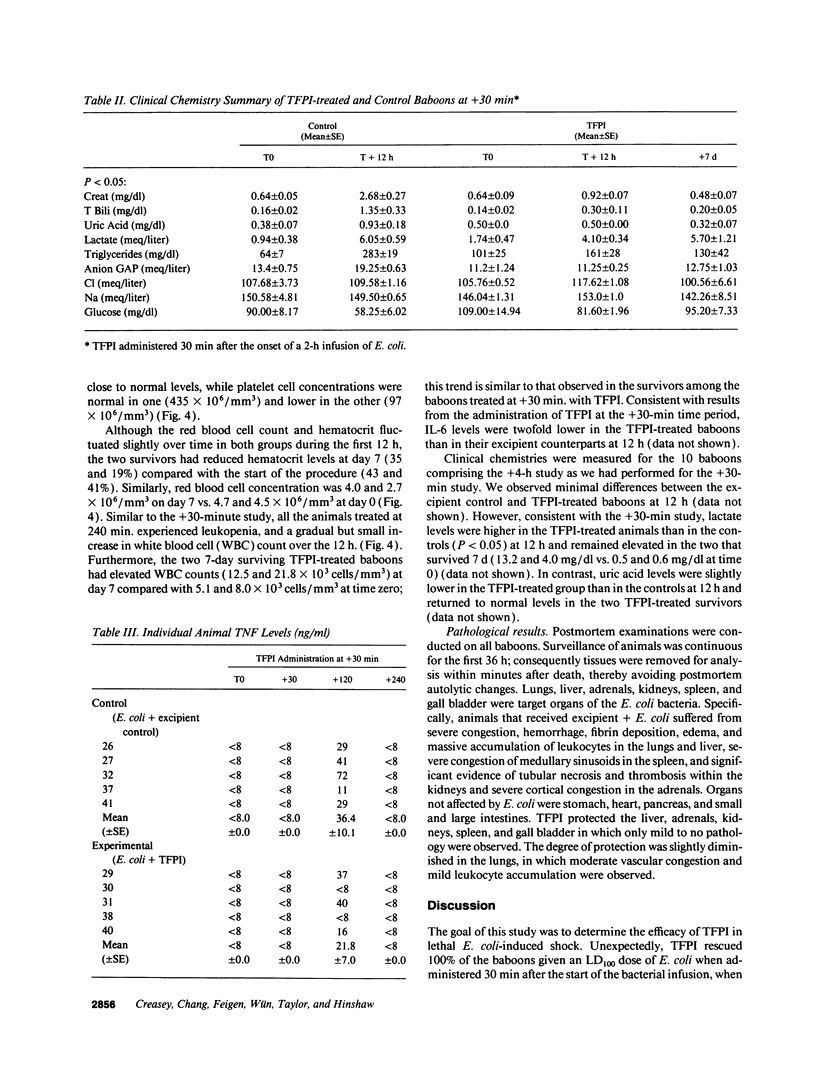
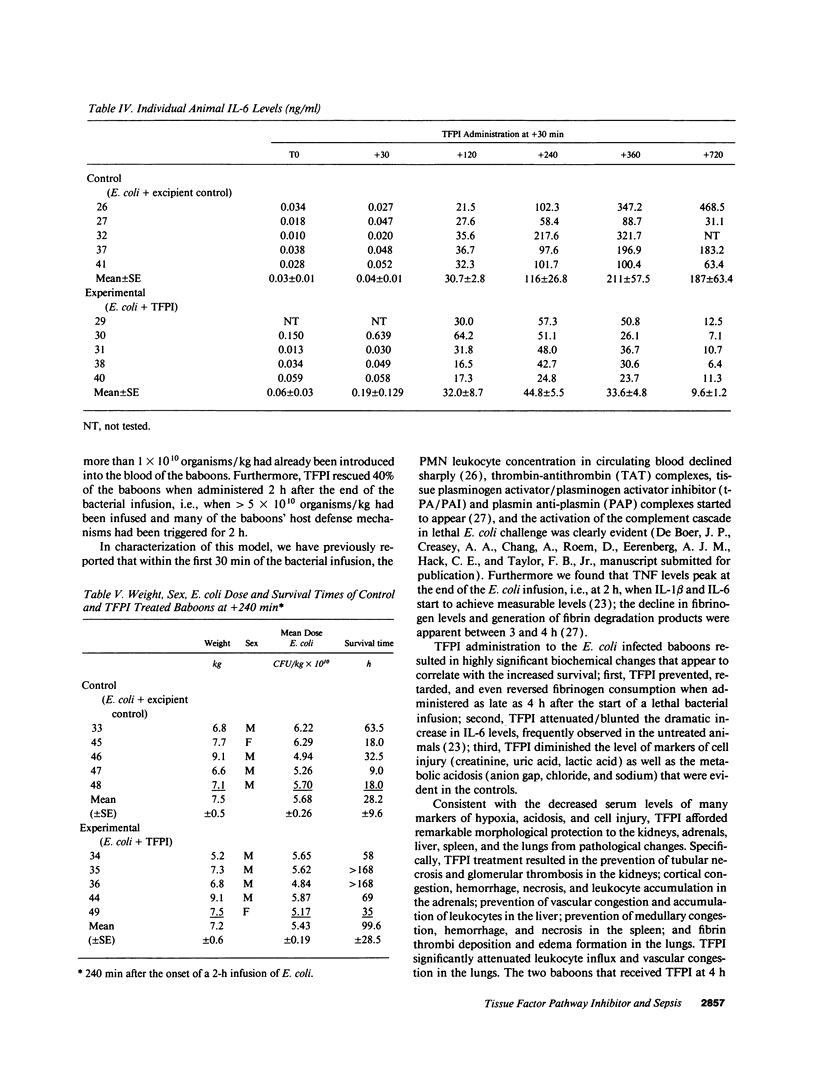
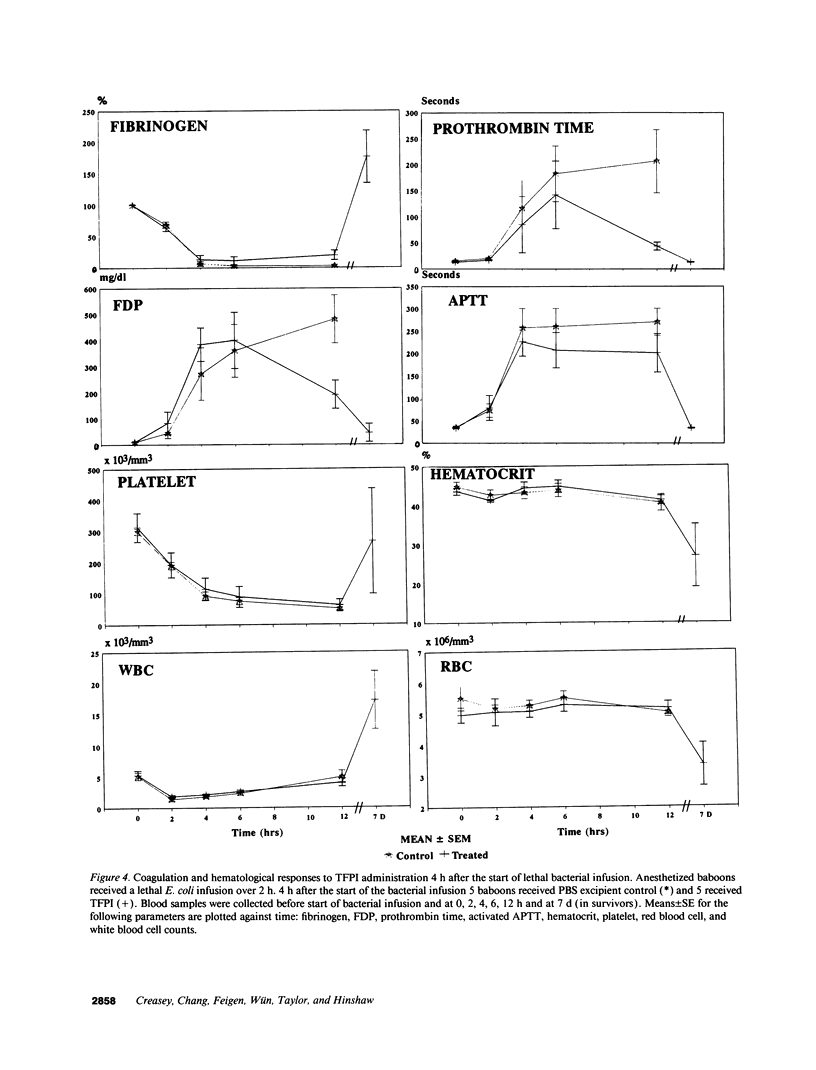
This study was designed to test the hypothesis that tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) plays a significant role in vivo in regulating coagulation that results from exposure of blood to tissue factor after vascular injury as in the case of gram negative sepsis. Highly purified recombinant TFPI (6 mg/kg) was administered either 30 min or 4 h after the start of a lethal intravenous Escherichia coli infusion in baboons. Early posttreatment of TFPI resulted in (a) permanent seven-day survivors (5/5) with significant improvement in quality of life, while the mean survival time for the controls (5/5) was 39.9 h (no survivors); and (b) significant attenuations of the coagulation response and various measures of cell injury, with significant reductions in pathology observed in E. coli sepsis target organs, including kidneys, adrenals, and lungs. TFPI administration did not affect the reduction in mean systemic arterial pressure, the increases in respiration and heart rate, or temperature changes associated with the bacterial infusion. TFPI treated E. coli infected baboons had significantly lower IL-6 levels than their phosphate buffered saline-treated controls, however tumor necrosis factor levels were similarly elevated in both groups. In contrast to the earlier 30-min treatment, the administration of TFPI at 4 h, i.e., 240 min, after the start of bacterial infusion resulted in prolongation of survival time, with 40% survival rate (2/5) and some attenuation of the coagulopathic response, especially in animals in which fibrinogen levels were above 10% of normal at the time of TFPI administration. Results provide evidence for the significance of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in bacterial sepsis, and suggest a role for blood coagulation in the regulation of the inflammatory response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ameri A., Kuppuswamy M. N., Basu S., Bajaj S. P. Expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor by cultured endothelial cells in response to inflammatory mediators. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3219–3226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj M. S., Kuppuswamy M. N., Saito H., Spitzer S. G., Bajaj S. P. Cultured normal human hepatocytes do not synthesize lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor: evidence that endothelium is the principal site of its synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Fiers W., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen W. M., Wu H. F., Featherstone G. L., Jenzano J. W., Lundblad R. L. Linkage between blood coagulation and inflammation: stimulation of neutrophil tissue kallikrein by thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90926-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey A. A., Stevens P., Kenney J., Allison A. C., Warren K., Catlett R., Hinshaw L., Taylor F. B., Jr Endotoxin and cytokine profile in plasma of baboons challenged with lethal and sublethal Escherichia coli. Circ Shock. 1991 Feb;33(2):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day K. C., Hoffman L. C., Palmier M. O., Kretzmer K. K., Huang M. D., Pyla E. Y., Spokas E., Broze G. J., Jr, Warren T. G., Wun T. C. Recombinant lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor inhibits tissue thromboplastin-induced intravascular coagulation in the rabbit. Blood. 1990 Oct 15;76(8):1538–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberger P., Sörskog L., Nilsson K., Knös M. The use of a quantitative assay in endotoxin testing. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;231:149–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard T. J., Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Likert K. M., Brown S. G., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Functional significance of the Kunitz-type inhibitory domains of lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):518–520. doi: 10.1038/338518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Archer L. T., Beller-Todd B. K., Coalson J. J., Flournoy D. J., Passey R., Benjamin B., White G. L. Survival of primates in LD100 septic shock following steroid/antibiotic therapy. J Surg Res. 1980 Feb;28(2):151–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Brackett D. J., Archer L. T., Beller B. K., Wilson M. F. Detection of the 'hyperdynamic state' of sepsis in the baboon during lethal E. coli infusion. J Trauma. 1983 May;23(5):361–365. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198305000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Cross A. S. Interleukin-6 is a better marker of lethality than tumor necrosis factor in endotoxin treated mice. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Aug;4(6):317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg T., Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A., Prydz H. Cellular cooperation in endothelial cell thromboplastin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jan;53(1):85–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Berghaus G. Pathophysiologic and biochemical events in disseminated intravascular coagulation: dysregulation of procoagulant and anticoagulant pathways. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1989 Jan;15(1):58–87. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Brown S. G., Miletich J. P., Rader D. J., Broze G. J., Jr Plasma antigen levels of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor in patient samples. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Purification and characterization of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18832–18837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Flaegstad T. Increased tissue thromboplastin activity in monocytes of patients with meningococcal infection: related to an unfavourable prognosis. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Feb 28;49(1):5–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmier M. O., Hall L. J., Reisch C. M., Baldwin M. K., Wilson A. G., Wun T. C. Clearance of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):33–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport S. I. The extrinsic pathway inhibitor: a regulator of tissue factor-dependent blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):6–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers R. P., Hathaway W. E., Weston W. L. The endotoxin-induced coagulant activity of human monocytes. Br J Haematol. 1975 Jul;30(3):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandset P. M., Røise O., Aasen A. O., Abildgaard U. Extrinsic pathway inhibitor in postoperative/posttraumatic septicemia: increased levels in fatal cases. Haemostasis. 1989;19(4):189–195. doi: 10.1159/000215916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandset P. M., Warn-Cramer B. J., Rao L. V., Maki S. L., Rapaport S. I. Depletion of extrinsic pathway inhibitor (EPI) sensitizes rabbits to disseminated intravascular coagulation induced with tissue factor: evidence supporting a physiologic role for EPI as a natural anticoagulant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. B., Jr, Chang A. C., Peer G. T., Mather T., Blick K., Catlett R., Lockhart M. S., Esmon C. T. DEGR-factor Xa blocks disseminated intravascular coagulation initiated by Escherichia coli without preventing shock or organ damage. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. B., Jr, Chang A., Esmon C. T., D'Angelo A., Vigano-D'Angelo S., Blick K. E. Protein C prevents the coagulopathic and lethal effects of Escherichia coli infusion in the baboon. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):918–925. doi: 10.1172/JCI112902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. B., Jr, Chang A., Ruf W., Morrissey J. H., Hinshaw L., Catlett R., Blick K., Edgington T. S. Lethal E. coli septic shock is prevented by blocking tissue factor with monoclonal antibody. Circ Shock. 1991 Mar;33(3):127–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. B., Jr, Emerson T. E., Jr, Jordan R., Chang A. K., Blick K. E. Antithrombin-III prevents the lethal effects of Escherichia coli infusion in baboons. Circ Shock. 1988 Nov;26(3):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr T. A., Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in rabbits induced by administration of endotoxin or tissue factor: effect of anti-tissue factor antibodies and measurement of plasma extrinsic pathway inhibitor activity. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1481–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Kretzmer K. K., Palmier M. O., Day K. C., Huang M. D., Welsch D. J., Lewis C., Wolfe R. A., Zobel J. F., Lange G. W. Comparison of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitors expressed in human SK hepatoma, mouse C127, baby hamster kidney, and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):54–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer J. P., Creasy A. A., Chang A., Roem D., Brouwer M. C., Eerenberg A. J., Hack C. E., Taylor F. B., Jr Activation patterns of coagulation and fibrinolysis in baboons following infusion with lethal or sublethal dose of Escherichia coli. Circ Shock. 1993 Jan;39(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


