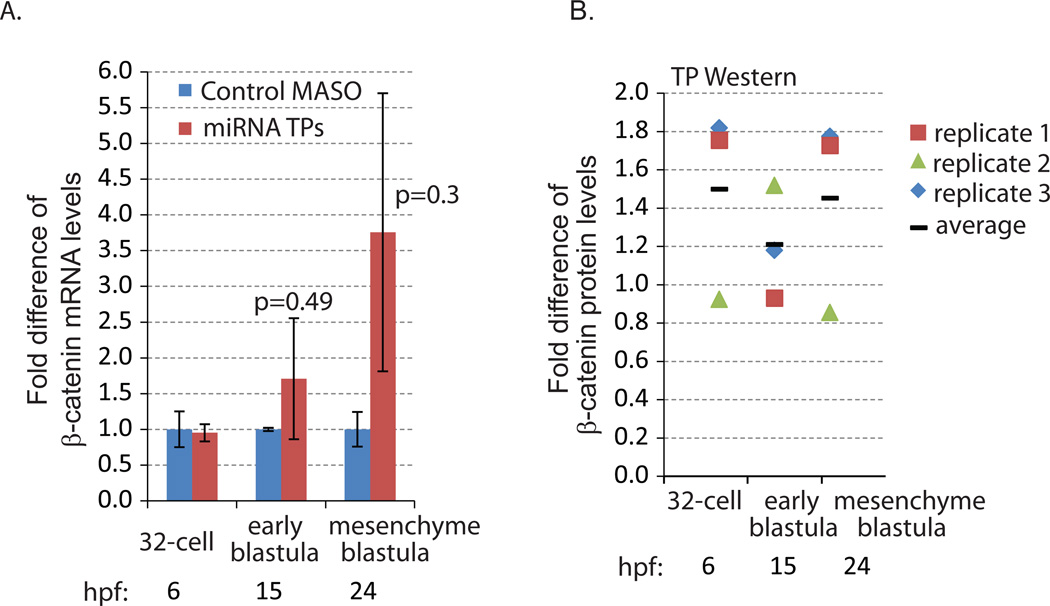
Fig. 3. β-catenin miRNA TP induced increased β-catenin protein and mRNA levels.
(A) qPCR was used to measure the transcript levels of β-catenin in the embryos injected with control and miRNA TP MASOs against the three functional miRNA binding sites. 100 embryos were collected at the 32-cell (6 hpf), early blastula (15 hpf) and mesenchyme blastula (24 hpf) stages. The mRNA level of β-catenin was increased at early blastula and mesenchyme blastula stages when miRNA regulation of β-catenin was abolished. However, these increases were not significant in β-catenin miRNA TP and control MASO-treated embryos (Student T-test). Hpf = hours post fertilization. (B) Western blot of 200 embryos injected with control or miRNA TPs. The embryos were collected at the 32-cell (6 hpf), early blastula (15 hpf) and mesenchyme blastula (24 hpf) stages. Compared to control embryos, embryos injected with miRNA TPs accumulated on average 1.5 times more β-catenin protein at the 32-cell and mesenchyme blastula stages. β-catenin protein levels are normalized to actin (3 biological replicates). Individual data points were indicated by the different icons. The average is graphed as a black bar.