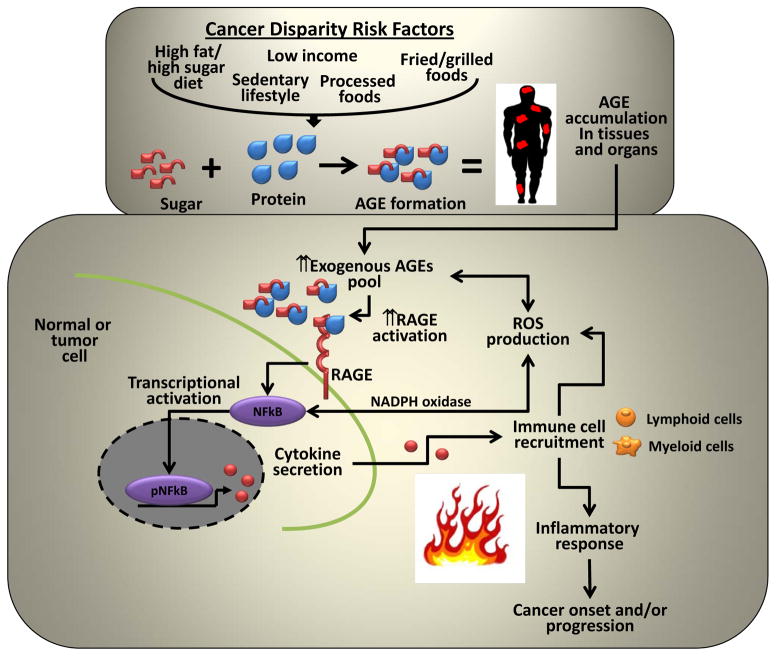
Figure 1. Hypothetical model for AGE mediated activation of inflammatory response in tumors.
Cancer disparity risk factors contribute to the increased exogenous AGE pool in our tissues and organs leading to the increased expression and activation of its cognate receptor RAGE. RAGE activation in turn triggers the activation of inflammatory associated transcription factors such as NFkB, STAT3 and HIF1α which increases cytokine secretion leading to the increased recruitment of lymphoid and myeloid immune cells into the tumor microenvironment, elevated ROS production and an inflammatory response. To perpetuate the cycle, reactive intermediates generated during AGE formation can directly increase ROS production to further promote the immune response. Oxidizing conditions and ROS presence can in turn further promote the formation of AGEs to create a cyclic and persistent oxidative response.