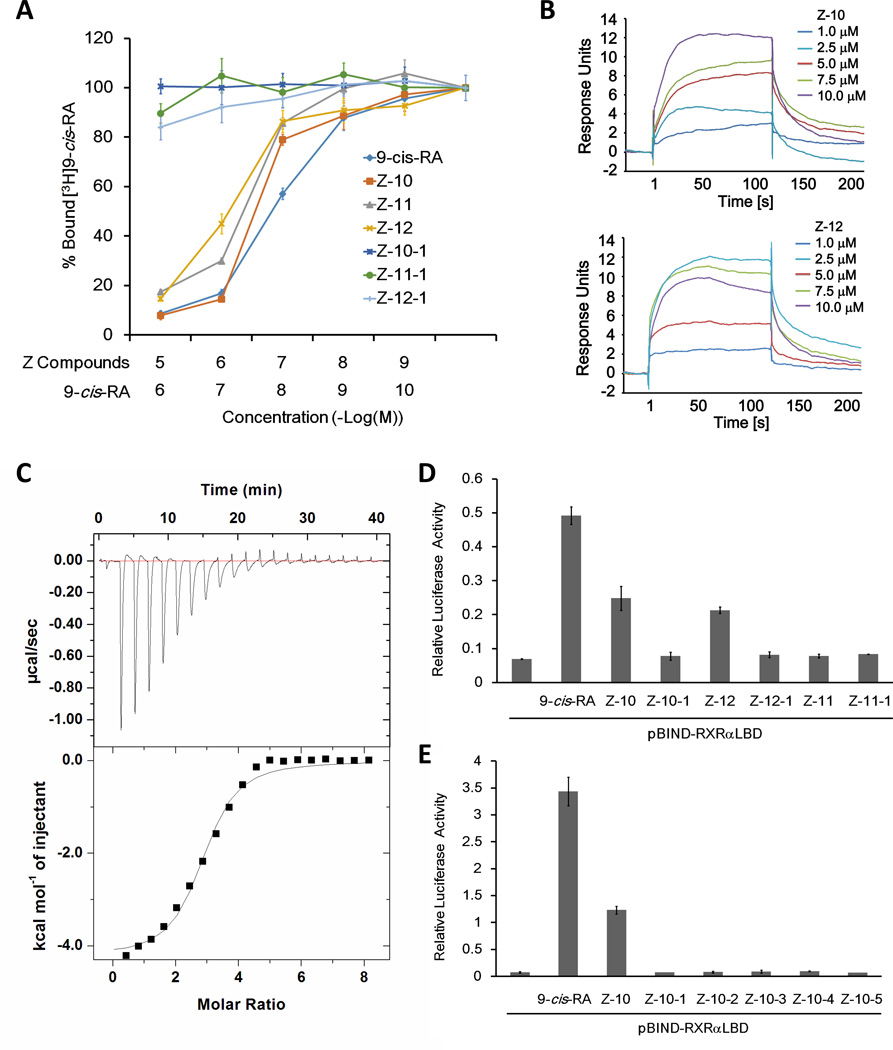
Figure 2. Nitro group is required for Z-10 and Z-12 binding to RXRα-LBD.
(A) Z-10, Z-11 and Z-12 but not their carboxyl derivatives compete with 9-cis-RA binding to RXRα in vitro. RXRα-LBD protein was incubated with [3H]9-cis-RA in the presence of the indicated compounds with different concentrations. Bound [3H]9-cis-RA was quantitated by liquid scintillation counting. (B) The binding of Z-10 and Z-12 to RXRα-LBD is evaluated by SPR assay. The sensorgrams were obtained from injection of a series of concentration of Z-10 and Z-12 over the immobilized RXRα-LBD Chip. BIA evaluation software was used to determine the equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd). (C) The thermodynamic property of Z-10 binding to RXRα-LBD is investigated by ITC assay. The upper curve in the panel showed the measured heats for each injection, while the lower plot shows the enthalpies for each injection along with the fit to a single binding site model used to estimate the Kd. All ITC data were analyzed using Origin software. (D–E) Nitro group is essential for Z-10 and Z-12 to induce RXRα transcriptional activity. pBIND-RXRαLBD and pG5-luc reporter were transiently transfected into HEK293T cells. Cells were treated with 9-cis-RA (0.1 µM), Z compounds (5 µM) and their derivatives (5 µM). Luciferase activities were measured and normalized. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. SPR, surface plasmon resonance; ITC, isothermal titration calorimetry.