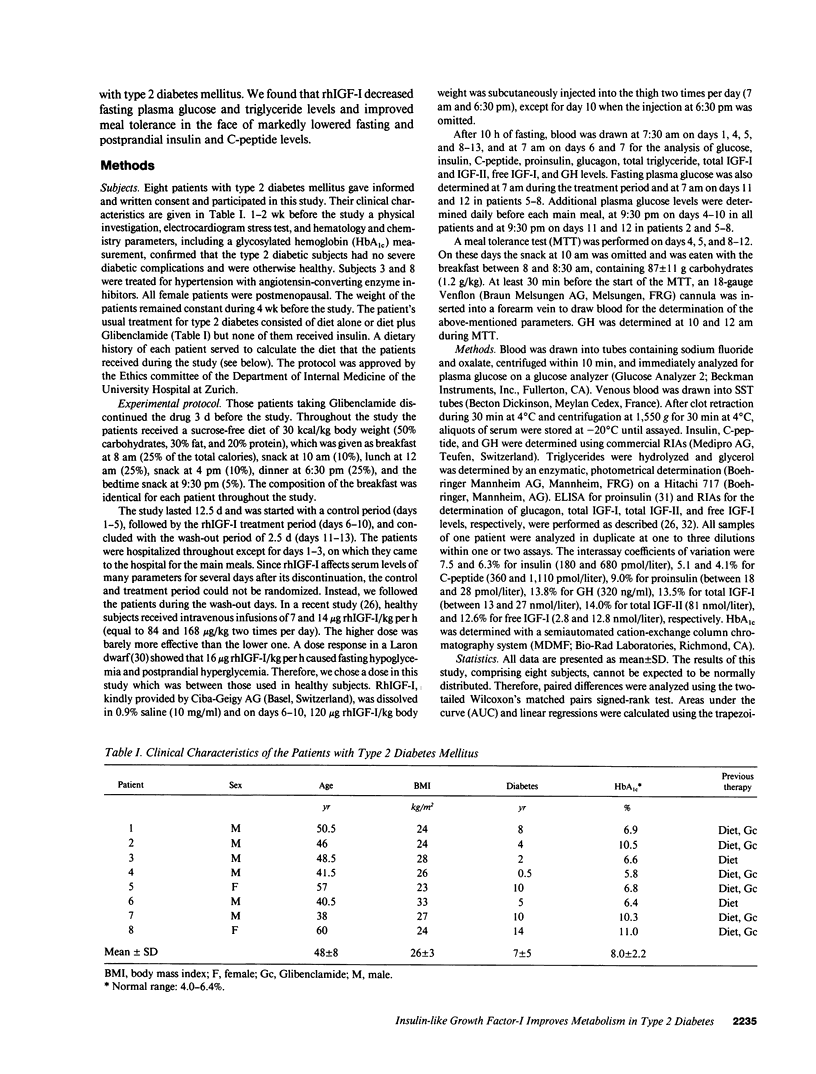
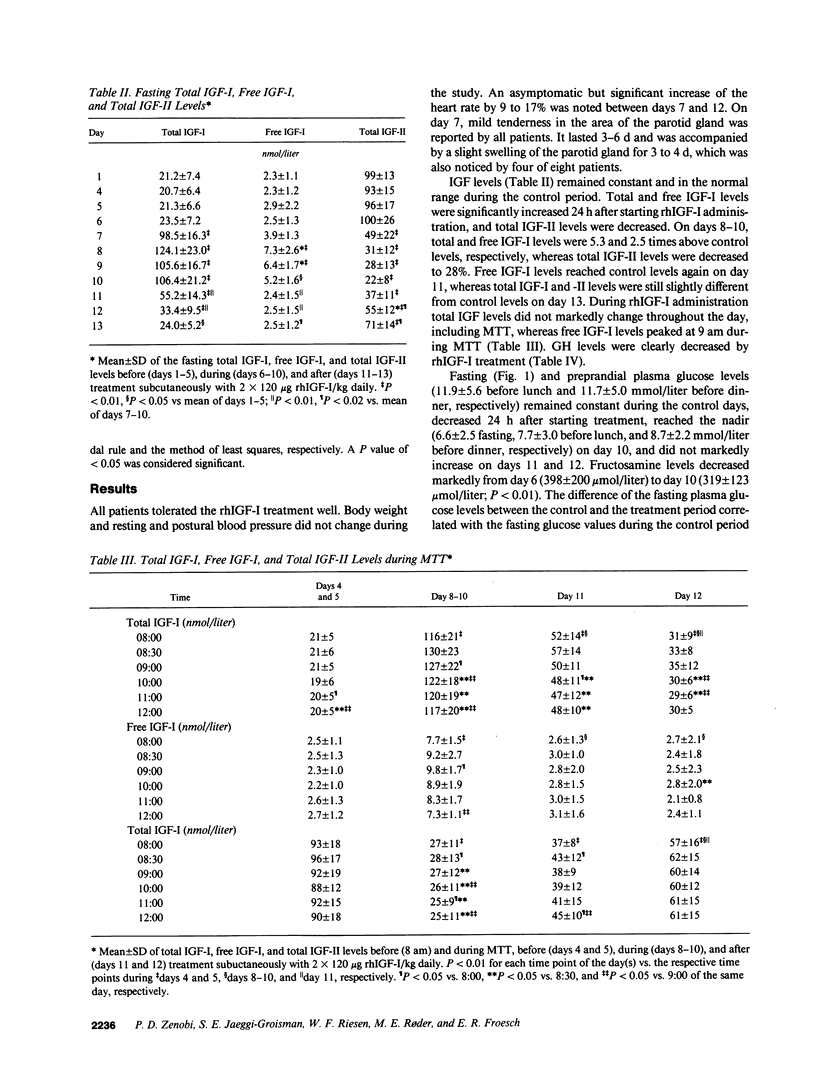
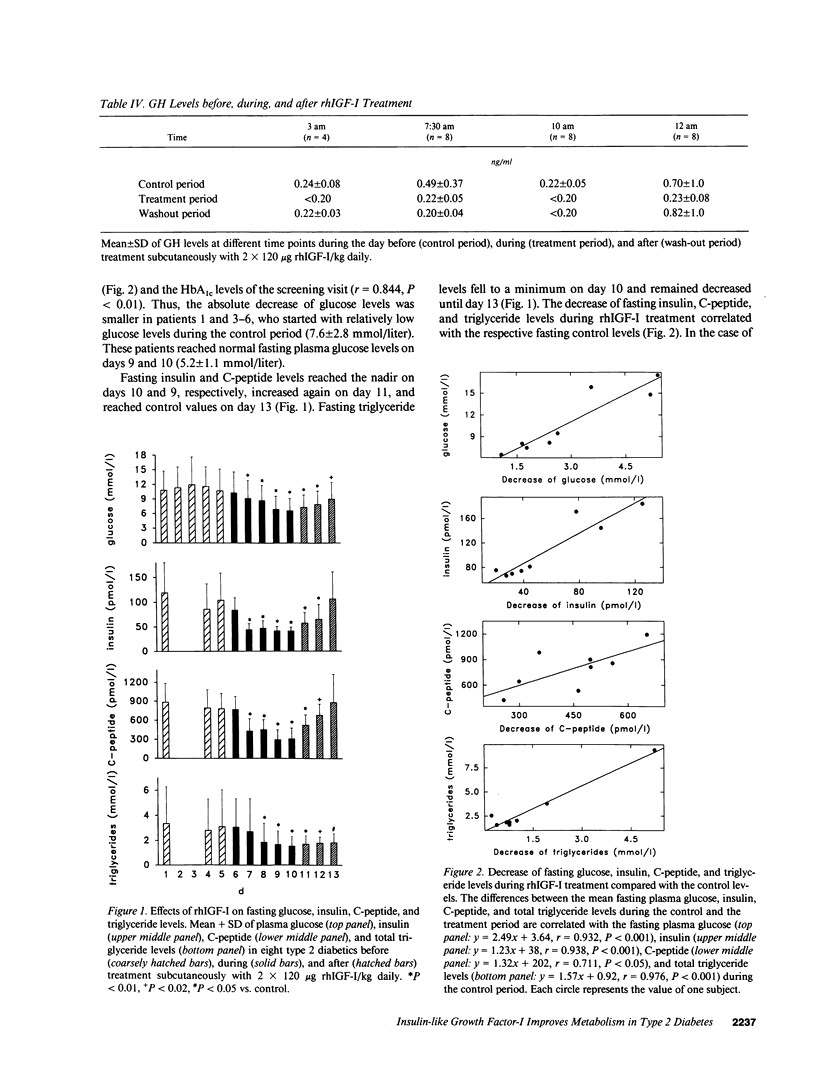
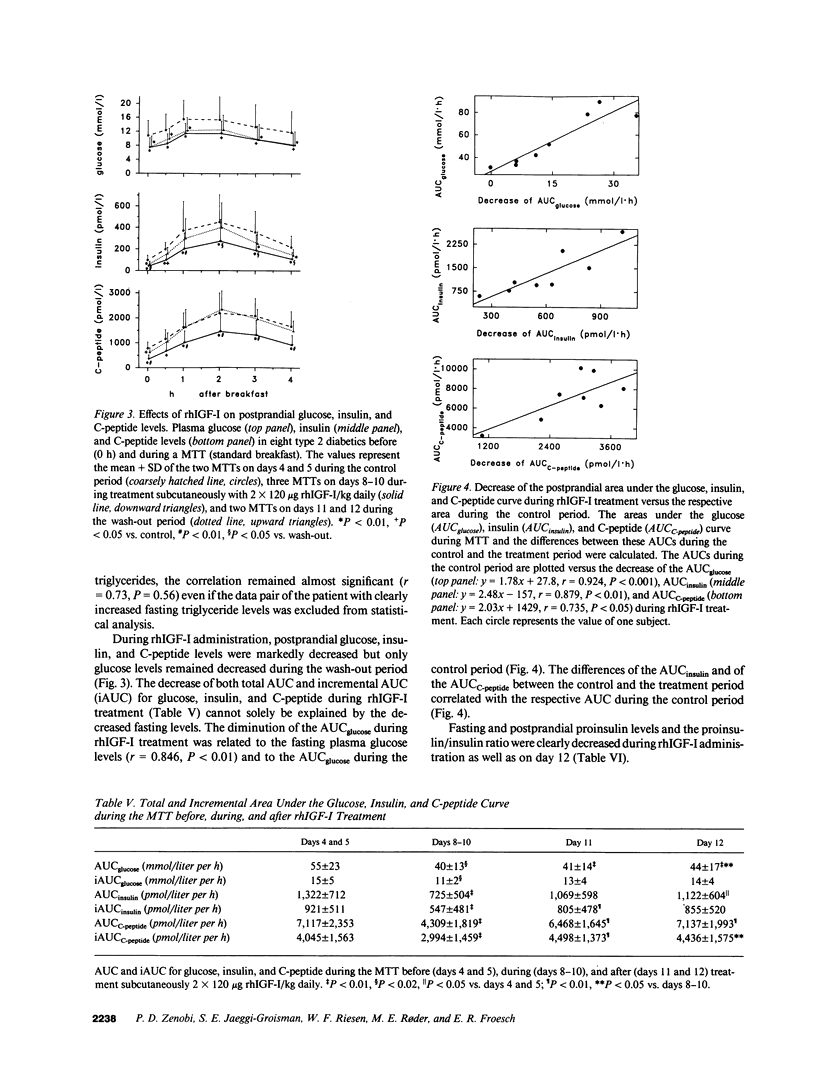
Abstract
Hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance cause vascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dietary treatment alone often fails and oral drugs or insulin enhance hyperinsulinemia. In previous studies, an intravenous bolus of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I (rhIGF-I) caused normoglycemia in insulin-resistant diabetics whereas rhIGF-I infusions lowered insulin and lipid levels in healthy humans, suggesting that rhIGF-I is effective in insulin-resistant states. Thus, eight type 2 diabetics on a diet received on five treatment days subcutaneous rhIGF-I (2 x 120 micrograms/kg) after five control days. Fasting and postprandial glucose, insulin, C-peptide, proinsulin, glucagon, triglyceride, insulin-like growth factor-I and -II, and growth hormone levels were determined. RhIGF-I administration increased total IGF-I serum levels 5.3-fold above control. During the control period mean (+/- SD) fasting glucose, insulin, C-peptide, and total triglyceride levels were 11.0 +/- 4.3 mmol/liter, 108 +/- 50 pmol/liter, 793 +/- 250 pmol/liter, and 3.1 +/- 2.7 mmol/liter, respectively, and decreased during treatment to a nadir of 6.6 +/- 2.5 mmol/liter, 47 +/- 18 pmol/liter, 311 +/- 165 pmol/liter, and 1.6 +/- 0.8 mmol/liter (P < 0.01), respectively. Postprandial areas under the glucose, insulin, and C-peptide curve decreased to 77 +/- 13 (P < 0.02), 52 +/- 11, and 60 +/- 9% (P < 0.01) of control, respectively. RhIGF-I decreased the proinsulin/insulin ratio whereas glucagon levels remained unchanged. The magnitude of the effects of rhIGF-I correlated with the respective control levels. Since rhIGF-I appears to improve insulin sensitivity directly and/or indirectly, it may become an interesting tool in type 2 diabetes and other states associated with insulin resistance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar-Parada E., Eisentraut A. M., Unger R. H. Pancreatic glucagon secretion in normal and diabetic subjects. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Jun;257(6):415–419. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196906000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenis G., Livingston J. N. Alterations in the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor produced by in vitro hyperinsulinemia. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Clemmons D. R., Boes M., Busby W. H., Booth B. A., Dake B. L., Sandra A. Transcapillary permeability and subendothelial distribution of endothelial and amniotic fluid insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the rat heart. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1078–1086. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barakat H. A., Carpenter J. W., McLendon V. D., Khazanie P., Leggett N., Heath J., Marks R. Influence of obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, and NIDDM on LDL structure and composition. Possible link between hyperinsulinemia and atherosclerosis. Diabetes. 1990 Dec;39(12):1527–1533. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.12.1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulinlike growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI112742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornfeldt K. E., Gidlöf R. A., Wasteson A., Lake M., Skottner A., Arnqvist H. J. Binding and biological effects of insulin, insulin analogues and insulin-like growth factors in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Comparison of maximal growth promoting activities. Diabetologia. 1991 May;34(5):307–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00405001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. J., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Quantification of the relative impairment in actions of insulin on hepatic glucose production and peripheral glucose uptake in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1988 Jan;37(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Jun;37(6):667–687. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Soman V., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Insulin binding to monocytes and insulin action in human obesity, starvation, and refeeding. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):204–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI109108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Dills D. G., Moss S. E., Klein R., Klein B. E. Association of elevated IGF-I levels with increased retinopathy in late-onset diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Dec;40(12):1725–1730. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.12.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills D. G., Moss S. E., Klein R., Klein B. E., Davis M. Is insulinlike growth factor I associated with diabetic retinopathy? Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):191–195. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feek C. M., Bevan J. S., Taylor S., Brown N. S., Baird J. D. The effect of bromocriptine on insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in patients with acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Nov;15(5):473–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Haffner S. M., Mitchell B. D., Stern M. P. Hyperinsulinaemia: the key feature of a cardiovascular and metabolic syndrome. Diabetologia. 1991 Jun;34(6):416–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00403180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firth R., Bell P., Marsh M., Rizza R. A. Effects of tolazamide and exogenous insulin on pattern of postprandial carbohydrate metabolism in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Results of randomized crossover trial. Diabetes. 1987 Oct;36(10):1130–1138. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.10.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontbonne A. M., Eschwège E. M. Insulin and cardiovascular disease. Paris Prospective Study. Diabetes Care. 1991 Jun;14(6):461–469. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser B., Leibovich G., Nesher R., Hartling S., Binder C., Cerasi E. Improved beta-cell function after intensive insulin treatment in severe non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Jul;118(3):365–373. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. B., Guay C., Marsh R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates proliferation, migration, and plasminogen activator release by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 1990 Apr;9(4):323–335. doi: 10.3109/02713689008999620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Schmid C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor I on insulin secretion and renal function in normal human subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2868–2872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Dec;121(6):753–758. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutniak M., Karlander S. G., Efendić S. Glyburide decreases insulin requirement, increases beta-cell response to mixed meal, and does not affect insulin sensitivity: effects of short- and long-term combined treatment in secondary failure to sulfonylurea. Diabetes Care. 1987 Sep-Oct;10(5):545–554. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.5.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Gourmelen M., Noguiez P., Seurin D., Roghani M., Le Bouc Y., Povoa G., Merimee T. J., Hossenlopp P., Binoux M. Molecular forms of serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins in man: relationships with growth hormone and IGFs and physiological significance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec;69(6):1291–1301. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-6-1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartling S. G., Dinesen B., Kappelgård A. M., Faber O. K., Binder C. ELISA for human proinsulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 May 15;156(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. R., Wallace P., Olefsky J. M. Effects of weight loss on mechanisms of hyperglycemia in obese non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1986 Sep;35(9):990–998. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.9.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Sherwin R. S., Bowen L., Fryburg D., Fagin K. D., Tamborlane W. V., Shulman G. I. Metabolic effects of IGF-I and insulin in spontaneously diabetic BB/w rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):E262–E268. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.2.E262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Barrett E., Plewe G., Fagin K. D., Sherwin R. S. Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. Comparison with insulin. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1717–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI114072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., McCartney P., Keen H. The Bedford survey: ten year mortality rates in newly diagnosed diabetics, borderline diabetics and normoglycaemic controls and risk indices for coronary heart disease in borderline diabetics. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00254833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Roul C., Alessi M. C., Ardissone J. P., Heim M., Vague P. Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor activity in non insulin dependent diabetic patients--relationship with plasma insulin. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Jun 30;61(3):370–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberton R. P., Goodman A. D., Kassoff A., Rubin C. L., Treble D. H., Saba T. M., Merimee T. J., Dodds W. J. Von Willebrand factor (VIII R:Ag), fibronectin, and insulin-like growth factors I and II in diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):125–129. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Vandekerkhove K. M. Insulin-like growth factor-I at physiological concentrations is a potent inhibitor of insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1593–1598. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston N., Pollare T., Lithell H., Arner P. Characterisation of insulin-like growth factor I receptor in skeletal muscles of normal and insulin resistant subjects. Diabetologia. 1988 Dec;31(12):871–877. doi: 10.1007/BF00265369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity and noninsulin-dependent (type II) diabetes. Am J Med. 1981 Jan;70(1):151–168. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90422-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi C., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Freychet P. Effects and binding of insulin-like growth factor I in the isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice: comparison with insulin. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):723–730. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Banting lecture 1990. Beta-cells in type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1991 Feb;40(2):166–180. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Genest J., Baker B. A., Gerich J. E. Production of insulin resistance by hyperinsulinaemia in man. Diabetologia. 1985 Feb;28(2):70–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00279918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Smith D., Shulman G. I., Papachristou D., DeFronzo R. A. Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1510–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI112981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymaszewski Z., Cohen R. M., Chomczynski P. Human growth hormone stimulates proliferation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E. J., Zenobi P. D., Torresani T., Werder E. A., Zachmann M., Froesch E. R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I (rhIGF I) reduces hyperglycaemia in patients with extreme insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 1991 Sep;34(9):675–679. doi: 10.1007/BF00400998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha M. K., Buchanan C., Leggett N., Martin L., Khazanie P. G., Dimarchi R., Pories W. J., Caro J. F. Mechanism of IGF-I-stimulated glucose transport in human adipocytes. Demonstration of specific IGF-I receptors not involved in stimulation of glucose transport. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1217–1225. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. K., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Dec;71(6):1632–1636. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-6-1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner G., Morita S., Vranic M. Resistance to insulin but not to glucagon in lean human hypertriglyceridemics. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):899–905. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suikkari A. M., Koivisto V. A., Koistinen R., Seppälä M., Yki-Järvinen H. Dose-response characteristics for suppression of low molecular weight plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein by insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Jan;68(1):135–140. doi: 10.1210/jcem-68-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönksen P. H., Greenwood F. C., Ellis J. P., Lowy C., Rutherford A., Nabarro J. D. Changes of carbohydrate tolerance in acromegaly with progress of the disease and in response to treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Oct;27(10):1418–1430. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-10-1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. L., Ginalska-Malinowska M., Romer T. E., Pucilowska J. B., Underwood L. E. Effects of the infusion of insulin-like growth factor I in a child with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome (Laron dwarfism). N Engl J Med. 1991 May 23;324(21):1483–1488. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105233242107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. M., Nissley S. P., Moses A. C., Rechler M. M., Johnsonbaugh R. E. The growth hormone dependence of a somatomedin-binding protein in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):49–57. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Guler H. P., Waldvogel M., Hauri C., Futo E., Hossenlopp P., Binoux M., Froesch E. R. Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in humans. Increased expression of IGF binding protein 2 during IGF I treatment of healthy adults and in patients with extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):952–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenobi P. D., Graf S., Ursprung H., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose tolerance, insulin levels, and insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1908–1913. doi: 10.1172/JCI115796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenobi P. D., Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors in the Göttinger miniature-pig. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Mar;117(3):343–352. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1170343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


