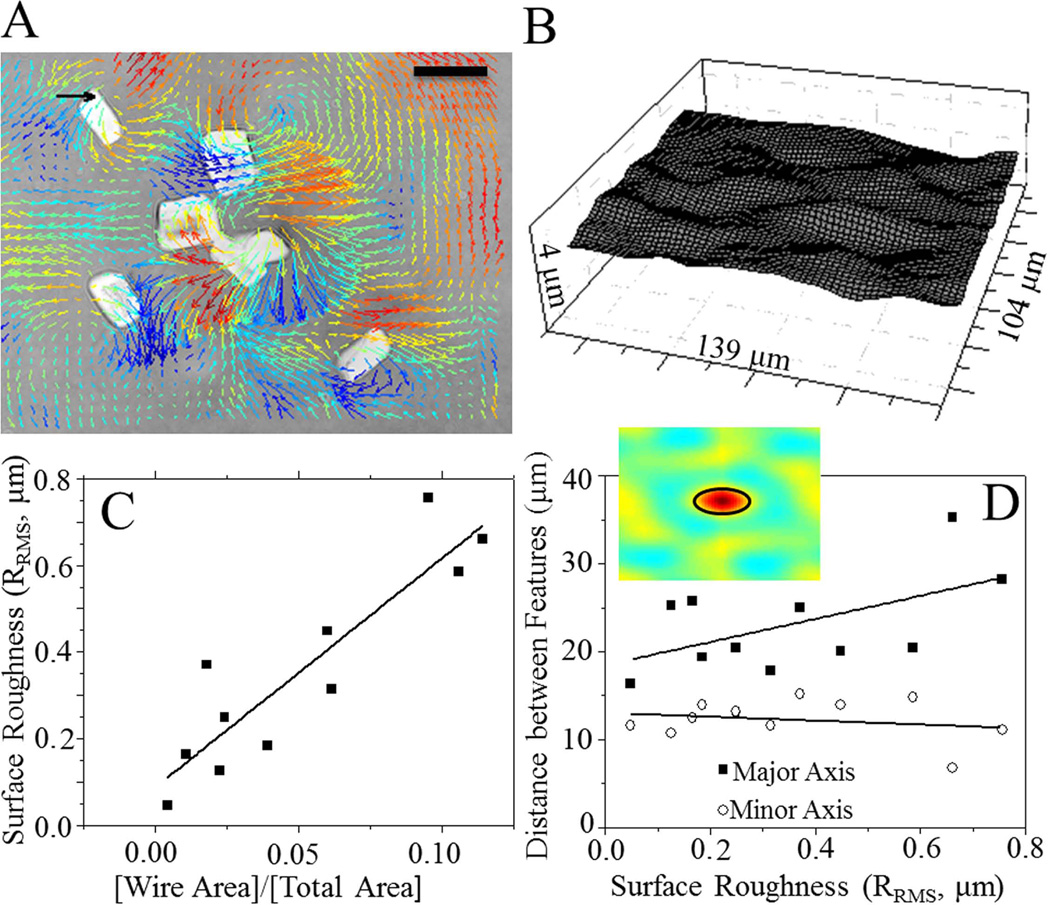
FIGURE 1.
Microwire-embedded matrix characterization. A: Displacement field induced by microwires in a 0.3 T magnetic field. Arrows indicate planar displacements whereas the color scale indicates z-displacements. Displacements were tracked by traction force microscopy (TFM) software. Warm (red) and cool (blue) colors correspond to positive and negative changes in z-relative to the undeformed surface. Scale bar = 20 µm. Black arrow = 5 µm displacement. B: Topographical map of surface feature changes. Features are on the order of 0.5–1.0 µm. C: A plot of the root-mean-square surface roughness (RRMS) versus wire density (wire area divided by total surface area within an image) shows a positive correlation (R2 = 0.81). D: Spatial correlation analysis showing the primary lobe that indicates the peak-to-valley distance between features (inset). The distance between features along the major and minor axis of each feature was plotted as a function of surface roughness with little change observed as a function of surface roughness. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]