Table 3.
Thrombolytic drugs data: results from consistency and inconsistency models. ‘REML’ is the data augmentation approach using h = 0.001, m = 0.08 and with 10 000 parametric bootstrap samples to compute P(best). ‘Bayes’ is the Bayesian approach and estimates are posterior means
| Consistency model | Inconsistency model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate (standard error) | P(best) | Estimate (standard error) | |||||
| Treatment | Parameter | REML | Bayes | REML | Bayes | REML | Bayes |
| A | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| B | δAB | −0.16 (0.05) | −0.23 (0.14) | 0.19 | 0.17 | −0.16 (0.22) | −0.16 (0.31) |
| C | δAC | 0.00 (0.03) | −0.02 (0.10) | 0.00 | 0.01 | −0.03 (0.22) | −0.03 (0.31) |
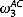 |
−0.16 (0.32) | −0.18 (0.38) | |||||
| D | δAD | −0.04 (0.05) | −0.06 (0.14) | 0.00 | 0.02 | −0.04 (0.22) | −0.04 (0.31) |
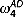 |
0.45 (0.73) | 0.48 (0.82) | |||||
| E | δAE | −0.16 (0.08) | −0.22 (0.22) | 0.23 | 0.28 | −0.15 (0.32) | −0.15 (0.45) |
| F | δAF | −0.11 (0.06) | −0.18 (0.16) | 0.07 | 0.11 | −0.06 (0.23) | −0.06 (0.32) |
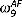 |
−0.18 (0.40) | −0.21 (0.52) | |||||
| G | δAG | −0.20 (0.22) | −0.23 (0.24) | 0.51 | 0.41 | −0.35 (0.55) | −0.37 (0.60) |
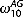 |
0.33 (0.71) | 0.38 (0.80) | |||||
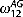 |
0.05 (0.69) | 0.05 (0.77) | |||||
| H | δAH | 0.01 (0.04) | 0.04 (0.11) | 0.00 | 0.04 | −0.00 (0.22) | −0.00 (0.30) |
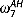 |
−0.06 (0.41) | −0.06 (0.47) | |||||
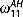 |
1.20 (0.53) | 1.25 (0.64) | |||||
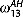 |
−0.31 (0.45) | −0.32 (0.52) | |||||
| Heterogeneity | τ | 0.02 (0.08) | 0.12 (0.10) | 0.22 (0.14) | 0.26 (0.15) | ||
Wald test of consistency (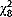 ) ) |
8.61 | 7.91 | |||||
| Deviance information criterion | 95.92 | 97.96 | |||||
