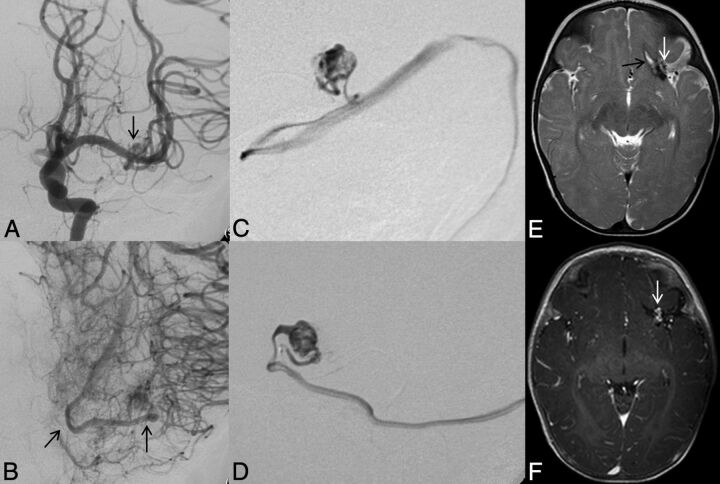
Fig 4.
Left ICA catheter angiogram (A and B), microcatheter injection (C and D), axial T2-weighted (E), and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR imaging (F) demonstrate imaging findings of a typical arteriovenous malformation. Anteroposterior projection of a left ICA injection demonstrates filling of the AVM nidus through an enlarged anterior temporal branch of the left MCA in the early arterial phase (A, arrow). There is arteriovenous shunting with early venous drainage through an enlarged left inferior temporal vein (B, arrows). Microcatheter injection in frontal (C) and lateral (D) projections demonstrates a typical glomerular well-defined compact nidus supplied by a single terminal arterial feeder with shunting into a dilated vein. MR imaging shows the superficial location of the AVM, with vascular flow voids seen on T2-weighted imaging (E, arrow) and enhancement on postgadolinium T1-weighted imaging (F, arrow). Evidence of previous hemorrhage related to AVM rupture, with a slit-like hematoma cavity in the left inferior frontal lobe, and surrounding hemosiderin staining (E, black arrow).