Figure 1.
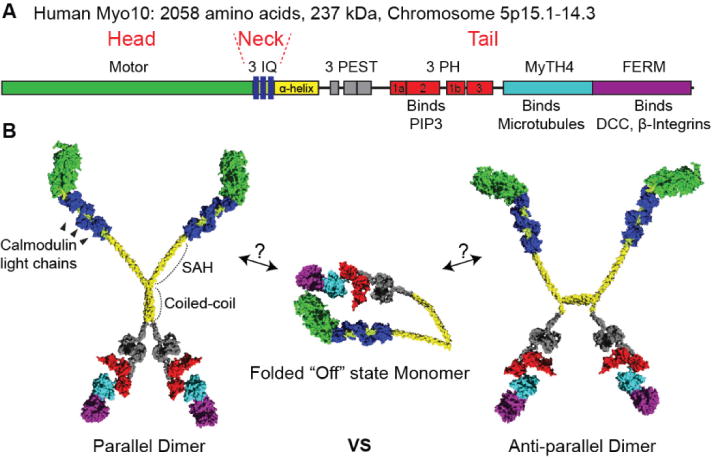
(A) Bar diagram of Myo10. The bar diagram highlights the domains of the Myo10 heavy chain. It has a head domain containing the motor, a neck domain containing three IQ motifs, and a tail domain containing numerous binding domains. The region containing 3 PH domains binds PIP3. The MyTH4-FERM domain is response for binding to microtubules and integrins. (B) Hypothetical models of Myo10 structure based on structure of individual domains. Myo10 monomers can form a folded “off” state where the tail domain folds over onto the head domain. Binding to PIP3 allows the folded monomers to form active dimers. Dimeric myosins were previously thought to form parallel heavy chain dimers, but recent data indicates that Myo10 can form anti-parallel dimers.
